In today’s digital age, data centers play a crucial role in storing and processing vast amounts of information. These facilities are the backbone of the internet, housing the servers and infrastructure that power our online activities. As data centers become increasingly important, there is a growing interest in exploring these facilities and understanding how they operate. Virtual tours offer a unique opportunity to get an inside look at data centers without physically visiting them. In this blog post, we will explore the benefits of virtual tours, the importance of data centers, how virtual tours work, and much more.
Key Takeaways
- Virtual tours of data centers offer a convenient way to explore these facilities from anywhere.
- Benefits of virtual tours include saving time and money, as well as gaining a better understanding of data centers.
- Data centers are crucial for storing and processing large amounts of data, and play a vital role in many industries.
- Virtual tours typically involve 360-degree views and detailed information about the infrastructure and technology used in data centers.
- Virtual tours can provide insights into security measures, different types of data centers, and the latest technologies being used.
The Benefits of Exploring Data Centers Virtually
One of the main advantages of virtual tours is that they provide a cost-effective alternative to physical tours. Visiting a data center in person can be expensive, especially if it requires travel or if the facility is located in a remote area. Virtual tours eliminate these costs by allowing users to explore data centers from the comfort of their own homes or offices. This makes it more accessible for individuals and businesses who are interested in learning about data centers but may not have the resources to visit them in person.
Another benefit of virtual tours is that they provide access to data centers that are not open to the public. Many data centers have strict security protocols in place and do not allow visitors due to the sensitive nature of the information they handle. Virtual tours offer a way for individuals to see these facilities without compromising security. This is particularly valuable for researchers, students, and professionals who want to gain insights into how data centers operate but do not have the opportunity to visit them physically.
Additionally, virtual tours offer convenience and flexibility. Users can explore data centers at their own pace and from any location with an internet connection. This means that they can fit the tour into their schedule without having to worry about travel arrangements or time constraints. Virtual tours also allow users to revisit certain areas or focus on specific aspects of the data center that they find most interesting. This level of flexibility is not possible with physical tours, making virtual tours a popular choice for those who want to learn about data centers on their own terms.
Understanding the Importance of Data Centers
Data centers are critical infrastructure that support the digital economy. They are responsible for storing, processing, and distributing vast amounts of data that power our everyday lives. From streaming videos and social media to online shopping and cloud computing, data centers enable the seamless delivery of digital services. Without data centers, many of the online activities we take for granted would not be possible.
The impact of data centers extends beyond individual users and businesses. They also play a crucial role in driving economic growth and innovation. Data centers create jobs, attract investment, and contribute to local economies. They provide the infrastructure needed for businesses to store and analyze data, enabling them to make informed decisions and develop new products and services. In addition, data centers support emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and the Internet of Things, which have the potential to transform industries and improve our quality of life.
As the demand for digital services continues to grow, so does the need for data centers. According to a report by Cisco, global data center traffic is expected to triple by 2022. This growth is driven by factors such as the increasing adoption of cloud computing, the proliferation of connected devices, and the rise of data-intensive applications. To meet this demand, data centers will need to expand their capacity and adopt new technologies and practices. Virtual tours provide a valuable opportunity to learn about these developments and gain insights into the future of data centers.
How Virtual Tours Work and What to Expect
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| What are Virtual Tours? | Virtual Tours are interactive simulations of real-world locations, usually composed of a sequence of videos or still images. They are often used in the real estate industry to showcase properties to potential buyers. |
| How do Virtual Tours work? | Virtual Tours work by stitching together multiple images or videos of a location to create a seamless, 360-degree view. Users can navigate through the tour using their mouse or touch screen, and often have the ability to zoom in and out or view additional information about specific features. |
| What are the benefits of Virtual Tours? | Virtual Tours allow potential buyers to view a property from anywhere in the world, at any time. They also provide a more immersive and engaging experience than traditional photos or videos, and can help to save time and money by reducing the need for in-person visits. |
| What should I expect from a Virtual Tour? | You should expect a high-quality, interactive experience that allows you to explore a property in detail. You may also have access to additional information, such as floor plans or property specifications, depending on the specific tour. |
Virtual tours use technology to create an immersive experience that simulates a physical visit to a data center. There are several ways in which virtual tours can be conducted, depending on the platform or software used. One common method is through the use of 360-degree panoramic images or videos. These images allow users to navigate through the data center and explore different areas by clicking and dragging their mouse or using touch gestures on a mobile device.
Virtual tours may also include interactive elements such as hotspots, which provide additional information or multimedia content when clicked. This can include videos, images, text descriptions, or links to related resources. Some virtual tours also offer guided tours, where a narrator or guide provides commentary and explanations as users navigate through the data center. This can enhance the educational value of the tour and provide a more engaging experience.
When taking a virtual tour of a data center, users can expect to see various aspects of the facility. This can include the server rooms, where rows of racks filled with servers are housed, as well as the cooling systems and power infrastructure that support them. Users may also get a glimpse of the security measures in place, such as surveillance cameras, access control systems, and fire suppression systems. Additionally, virtual tours may showcase the network infrastructure that connects the data center to the internet and other networks.
To have a successful virtual tour experience, it is important to have a stable internet connection and a device that supports the virtual tour software. Users should also be prepared to spend some time exploring the data center and taking advantage of any interactive features available. It can be helpful to have a basic understanding of data center operations and infrastructure beforehand to fully appreciate what is being shown during the tour.
Touring Data Centers from the Comfort of Your Home
One of the key advantages of virtual tours is that they allow for remote access to data centers. This is particularly valuable for individuals who are unable to visit data centers in person due to geographical constraints or other limitations. Virtual tours provide an opportunity to explore data centers from anywhere in the world, as long as there is an internet connection.
There are several data centers that offer virtual tours to the public. These tours can be accessed through the data center’s website or through third-party platforms that specialize in virtual tours. Some data centers may require users to sign up or provide their contact information before accessing the virtual tour, while others may offer it freely without any registration.
One example of a data center that offers virtual tours is Google’s data center in Lenoir, North Carolina. Google provides a 360-degree virtual tour of its facility, allowing users to explore the server rooms, cooling systems, and other areas of the data center. The tour also includes interactive elements such as videos and text descriptions that provide additional information about the facility.
To access virtual tours of data centers, users can simply visit the data center’s website and look for a section dedicated to virtual tours or a similar term. Alternatively, they can search for virtual tours of data centers on search engines or virtual tour platforms. It is worth noting that not all data centers offer virtual tours, so it may take some research to find ones that do.
Getting a Closer Look at Data Center Infrastructure
Data center infrastructure refers to the physical components and systems that support the operation of a data center. This includes everything from the building itself to the servers, cooling systems, power distribution units, and network equipment. Understanding data center infrastructure is crucial for gaining insights into how these facilities operate and how they ensure the availability and reliability of digital services.
One of the key components of data center infrastructure is the server room. This is where the servers are housed, typically in racks or cabinets. The server room is designed to provide a controlled environment with proper cooling, ventilation, and humidity levels to ensure optimal performance and prevent equipment failure. It is also equipped with fire suppression systems and other safety measures to protect the servers from physical damage.
Another important component of data center infrastructure is the cooling system. Data centers generate a significant amount of heat due to the operation of the servers. Cooling systems are responsible for removing this heat and maintaining the temperature within acceptable limits. This can be achieved through various methods, such as air conditioning, liquid cooling, or a combination of both. Efficient cooling is essential for preventing overheating and ensuring the longevity of the servers.
Power infrastructure is another critical aspect of data center infrastructure. Data centers require a reliable and uninterrupted power supply to operate. This is achieved through redundant power sources, backup generators, and uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems. These systems ensure that the servers and other equipment continue to receive power even in the event of a power outage or other disruptions.
Other components of data center infrastructure include network equipment, such as routers and switches, which enable connectivity between the data center and the internet or other networks. Additionally, data centers may have storage systems, such as network-attached storage (NAS) or storage area networks (SAN), for storing and managing large amounts of data.
Learning About the Latest Technologies in Data Centers
Data centers are constantly evolving to keep up with the increasing demands of the digital age. New technologies are being developed and implemented to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance performance. Virtual tours provide an opportunity to learn about these emerging technologies and gain insights into how they are shaping the future of data centers.
One example of an emerging technology in data centers is edge computing. Edge computing involves processing data closer to where it is generated, rather than sending it to a centralized data center. This reduces latency and improves response times, making it ideal for applications that require real-time processing, such as autonomous vehicles or industrial automation. Virtual tours can showcase how edge computing is implemented in data centers and provide insights into its benefits and challenges.
Another emerging technology in data centers is artificial intelligence (AI). AI can be used to optimize various aspects of data center operations, such as energy management, predictive maintenance, and security. Virtual tours can demonstrate how AI is integrated into data centers and provide examples of how it is being used to improve efficiency and reliability.
In addition to edge computing and AI, there are several other innovative technologies that are transforming data centers. These include software-defined networking (SDN), which allows for more flexible and scalable network infrastructure, and modular data center designs, which enable rapid deployment and expansion of data center capacity. Virtual tours can provide a firsthand look at these technologies and help users understand their impact on data center operations.
Discovering the Security Measures in Place at Data Centers
Security is a top priority for data centers due to the sensitive nature of the information they handle. Data centers store and process vast amounts of data, including personal and financial information, trade secrets, and intellectual property. Protecting this data from unauthorized access, theft, or damage is crucial for maintaining the trust of customers and ensuring the integrity of digital services.
Data centers employ a variety of security measures to safeguard their facilities and the data they house. These measures can include physical security, such as surveillance cameras, access control systems, and perimeter fencing. Data centers may also have security personnel on-site to monitor the facility and respond to any security incidents.
In addition to physical security, data centers implement various cybersecurity measures to protect against online threats. This can include firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption technologies. Data centers also have strict access controls in place to ensure that only authorized personnel can enter certain areas of the facility.
Virtual tours can provide insights into the security measures in place at data centers. Users can see firsthand how access control systems work, what types of surveillance cameras are used, and how physical barriers are implemented to prevent unauthorized entry. Virtual tours may also include information about cybersecurity measures, such as firewalls or encryption technologies, and explain how they protect against online threats.
Exploring the Different Types of Data Centers
Data centers come in different shapes and sizes, each serving a specific purpose and catering to different needs. Understanding the different types of data centers can provide insights into their unique characteristics and how they support the digital economy.
One common type of data center is the enterprise data center. Enterprise data centers are owned and operated by individual organizations to support their internal IT infrastructure. These data centers are typically located on-site or in close proximity to the organization’s headquarters. Enterprise data centers are designed to meet the specific needs of the organization and may include additional features such as disaster recovery capabilities or high levels of security.
Another type of data center is the colocation data center. Colocation data centers are facilities that provide space, power, cooling, and network connectivity for multiple organizations to house their servers and IT infrastructure. Colocation data centers offer a cost-effective solution for businesses that do not want to build and maintain their own data centers. They also provide access to redundant power and cooling systems, as well as high-speed internet connections.
Cloud data centers are another type of data center that has gained popularity in recent years. Cloud data centers are large-scale facilities that host virtualized servers and storage systems. They provide on-demand access to computing resources, such as processing power or storage capacity, over the internet. Cloud data centers are designed to be highly scalable and flexible, allowing users to easily scale up or down their resources based on their needs.
Each type of data center has its own unique characteristics and advantages. Virtual tours can provide insights into these differences and help users understand how each type of data center operates.
The Future of Virtual Tours for Data Centers
Virtual tours offer a unique opportunity to explore data centers and gain insights into their operations without physically visiting them. They provide a cost-effective alternative to physical tours, allow access to data centers that are not open to the public, and offer convenience and flexibility. Data centers play a crucial role in today’s digital age, storing and processing vast amounts of data that power our online activities. They have a significant impact on businesses and society, driving economic growth and innovation. As the demand for digital services continues to grow, so does the need for data centers. Virtual tours provide a valuable opportunity to learn about data centers and gain insights into their future.
Looking ahead, virtual tours are likely to become even more popular in the data center industry. As technology continues to advance, virtual tours may become more immersive and interactive, providing an even more realistic experience. Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies could be used to create virtual tours that simulate a physical visit to a data center, allowing users to interact with the environment and experience it in a more engaging way. Additionally, as the number of data centers continues to grow, virtual tours may become a standard practice for showcasing these facilities and attracting customers.
In conclusion, virtual tours of data centers offer a valuable opportunity to explore these critical infrastructure facilities and gain insights into their operations. They provide a cost-effective alternative to physical tours, allow access to data centers that are not open to the public, and offer convenience and flexibility. Data centers play a crucial role in today’s digital age, supporting the storage and processing of vast amounts of data. As the demand for digital services continues to grow, so does the need for data centers. Virtual tours provide a unique way to learn about these facilities and gain insights into their future. Whether you are a student, researcher, or professional in the IT industry, virtual tours of data centers can provide valuable knowledge and understanding of the inner workings of these facilities. They allow individuals to see the equipment, infrastructure, and security measures in place, giving them a firsthand look at the technology that powers our digital world. Additionally, virtual tours can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, making them accessible to a wide range of individuals regardless of their location. Overall, virtual tours of data centers offer a convenient and informative way to learn about these critical facilities and their role in our increasingly digital society.
If you’re interested in exploring the world of data centers further, you might want to check out this informative article on AI-powered data centers and their transformative impact on the industry’s future. The article delves into the cutting-edge technologies being utilized in these data centers and how they are revolutionizing the way businesses operate. To gain a deeper understanding of this exciting topic, click here.
FAQs
What are data center virtual tours?
Data center virtual tours are online tours that allow users to explore and view a data center facility remotely. These tours are typically interactive and provide a detailed look at the various components and infrastructure of the data center.
Why are data center virtual tours important?
Data center virtual tours are important because they allow users to gain a better understanding of the inner workings of a data center facility. This can be especially useful for those who are considering using a data center for their business needs or for those who are interested in learning more about data center technology.
What can I expect to see on a data center virtual tour?
On a data center virtual tour, you can expect to see various components of the data center infrastructure, such as servers, storage devices, networking equipment, and cooling systems. You may also see security measures, such as biometric scanners and surveillance cameras.
How do I access a data center virtual tour?
Data center virtual tours can typically be accessed through the website of the data center provider. Some providers may require users to register or provide contact information before accessing the tour.
Are data center virtual tours secure?
Data center virtual tours are typically secure and do not pose a risk to the data center facility or its infrastructure. However, users should always follow any guidelines or instructions provided by the data center provider to ensure the security of the facility.
In today’s digital age, data centers play a crucial role in storing, processing, and managing vast amounts of information. With the increasing reliance on technology and the growing demand for uninterrupted access to data, maximum uptime in data centers has become more important than ever before. This blog post aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the importance of maximum uptime in data centers and offer practical solutions to achieve it.
Key Takeaways
- Maximum uptime is crucial for data centers to ensure uninterrupted operations.
- Common causes of data center outages include power failures, cooling system malfunctions, and human error.
- Regular maintenance and upgrades can prevent outages and improve performance.
- Redundancy and backup solutions are essential for critical systems to minimize downtime.
- Monitoring and managing power and cooling systems can optimize performance and prevent issues.
Understanding the Importance of Maximum Uptime in Data Centers
Maximum uptime refers to the ability of a data center to remain operational and accessible to users without any interruptions or downtime. It is crucial for data centers to maintain maximum uptime because any disruption in service can have severe consequences for businesses and organizations that rely on them.
Data center downtime can result in significant financial losses, damage to reputation, and loss of customer trust. For businesses that rely on data centers to store critical information or run mission-critical applications, even a few minutes of downtime can have catastrophic consequences. In addition, downtime can lead to lost productivity, missed opportunities, and potential legal and regulatory issues.
Identifying Common Causes of Data Center Outages
There are several common causes of data center outages that can lead to downtime. These include power failures, cooling system failures, network failures, human error, natural disasters, and cyber attacks.
Power failures can occur due to equipment failure, utility outages, or inadequate power supply. Cooling system failures can result from equipment malfunction or inadequate cooling capacity. Network failures can be caused by hardware or software issues, connectivity problems, or cyber attacks. Human error, such as accidental equipment shutdown or misconfiguration, can also lead to downtime. Natural disasters like earthquakes, floods, or storms can cause physical damage to data centers. Lastly, cyber attacks such as DDoS attacks or ransomware attacks can disrupt data center operations.
Real-world examples of data center outages caused by these factors include the Amazon Web Services (AWS) outage in 2017, which was caused by a human error during routine maintenance, and the Delta Air Lines outage in 2016, which was caused by a power failure.
Conducting Regular Maintenance and Upgrades to Prevent Outages
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Downtime | The amount of time the system is unavailable due to maintenance or upgrades |
| Frequency of maintenance | How often maintenance is performed on the system |
| Number of upgrades | The number of upgrades performed on the system |
| Cost of maintenance and upgrades | The total cost of performing maintenance and upgrades on the system |
| Impact on system performance | The effect of maintenance and upgrades on the system’s performance |
Regular maintenance and upgrades are essential to prevent data center outages. By conducting routine inspections, testing, and maintenance activities, potential issues can be identified and addressed before they escalate into major problems.
Maintenance activities should include regular equipment inspections, cleaning, and lubrication. It is also important to perform regular firmware and software updates to ensure that systems are up to date and protected against vulnerabilities. Additionally, equipment should be periodically tested to ensure proper functioning.
Upgrades should be performed to replace outdated or faulty equipment with newer, more reliable models. This includes upgrading power distribution units (PDUs), uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems, cooling systems, and networking equipment. Upgrading to more energy-efficient equipment can also help reduce operational costs and improve overall performance.
Proactive maintenance and upgrades can help minimize the risk of unexpected failures and downtime, ensuring maximum uptime for data centers.
Implementing Redundancy and Backup Solutions for Critical Systems
Implementing redundancy and backup solutions is another crucial step in achieving maximum uptime in data centers. Redundancy refers to the duplication of critical systems or components to ensure that there is a backup in case of failure. Backup solutions involve regularly creating copies of data and storing them in separate locations.
Critical systems that should have redundancy and backup solutions in place include power systems, cooling systems, networking equipment, storage devices, and servers. Redundant power systems can include backup generators or multiple utility feeds. Redundant cooling systems can involve redundant air conditioning units or liquid cooling solutions. Redundant networking equipment can include multiple switches or routers. Redundant storage devices can involve RAID configurations or distributed storage systems. Redundant servers can include clustering or virtualization technologies.
Backup solutions should include regular data backups and offsite storage. This ensures that in the event of a system failure or data loss, data can be quickly restored from the backup copies.
Implementing redundancy and backup solutions provides an additional layer of protection against system failures and helps minimize downtime in the event of a failure.
Monitoring and Managing Power and Cooling Systems for Optimal Performance


Power and cooling systems are critical components of data centers that require careful monitoring and management to ensure optimal performance and maximum uptime.
Power systems should be monitored to ensure that they are operating within their designed capacity. This includes monitoring power usage, voltage levels, and load balancing. Power monitoring tools can provide real-time data on power consumption and help identify potential issues before they cause downtime.
Cooling systems should be monitored to ensure that they are maintaining the required temperature and humidity levels. This includes monitoring temperature sensors, airflow, and cooling capacity. Cooling monitoring tools can provide insights into the performance of cooling systems and help identify any inefficiencies or potential failures.
Best practices for managing power and cooling systems include regular inspections, cleaning, and maintenance activities. This includes cleaning air filters, checking for leaks, and ensuring proper airflow. It is also important to regularly test backup power systems and cooling redundancy to ensure they are functioning as intended.
By monitoring and managing power and cooling systems effectively, data centers can optimize performance, reduce the risk of failures, and maintain maximum uptime.
Developing and Testing Disaster Recovery Plans to Minimize Downtime
Developing and testing disaster recovery plans is crucial for minimizing downtime in the event of a major system failure or disaster. A disaster recovery plan outlines the steps to be taken to restore operations after a disruption.
Components of a disaster recovery plan include identifying critical systems, establishing recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs), defining roles and responsibilities, documenting procedures, and establishing communication protocols.
Regular testing of the disaster recovery plan is essential to ensure its effectiveness. This involves conducting simulated disaster scenarios and evaluating the response and recovery processes. Testing helps identify any gaps or weaknesses in the plan and allows for adjustments to be made before an actual disaster occurs.
By developing and testing a robust disaster recovery plan, data centers can minimize downtime and ensure a quick recovery in the event of a major system failure or disaster.
Training Staff on Best Practices for Data Center Operations and Maintenance
Well-trained staff is essential for maintaining maximum uptime in data centers. Training should cover best practices for data center operations and maintenance, including equipment handling, safety protocols, troubleshooting procedures, and emergency response.
Training should be provided to all staff members involved in data center operations, including technicians, engineers, and administrators. It should be conducted regularly to ensure that staff members are up to date with the latest technologies, procedures, and industry standards.
Benefits of well-trained staff include improved efficiency, reduced risk of human error, faster response times to issues, and increased overall reliability of data center operations.
Conducting Regular Risk Assessments to Identify Potential Threats to Uptime
Regular risk assessments are essential for identifying potential threats to uptime and implementing appropriate mitigation measures. Risk assessments involve identifying potential risks, evaluating their likelihood and impact, and developing strategies to minimize or eliminate them.
Types of risks that should be assessed include power failures, cooling system failures, network failures, natural disasters, cyber attacks, equipment failures, and human error. Risk assessments should also consider the potential impact of these risks on data center operations and prioritize them based on their severity.
Benefits of regular risk assessments include improved preparedness for potential disruptions, reduced downtime, enhanced security measures, and increased overall resilience of data center operations.
Investing in Advanced Monitoring and Analytics Tools for Early Detection of Issues
Investing in advanced monitoring and analytics tools can help data centers detect and address issues before they escalate into major problems. These tools provide real-time data on the performance of critical systems, allowing for proactive troubleshooting and maintenance.
Types of monitoring and analytics tools that are available include environmental monitoring systems, power monitoring systems, network monitoring systems, and predictive analytics software.
Benefits of advanced monitoring and analytics tools include improved visibility into data center operations, early detection of potential issues, reduced downtime, increased efficiency, and optimized resource allocation.
Partnering with Experienced Data Center Providers for Expert Support and Guidance
Partnering with experienced data center providers can provide businesses with expert support and guidance in achieving maximum uptime. Data center providers offer a range of services, including colocation, managed services, cloud services, and disaster recovery solutions.
Colocation services involve renting space in a data center facility and leveraging the provider’s infrastructure and expertise. Managed services involve outsourcing the management of data center operations to the provider. Cloud services involve accessing computing resources and storage over the internet. Disaster recovery solutions involve replicating data and applications to a secondary site for quick recovery in the event of a major system failure or disaster.
Choosing the right data center provider is crucial for ensuring maximum uptime. Factors to consider when selecting a provider include their track record, reputation, certifications, security measures, scalability, and customer support.
In conclusion, maximum uptime is crucial for data centers to ensure uninterrupted access to critical information and applications. By understanding the importance of maximum uptime and implementing best practices such as regular maintenance and upgrades, redundancy and backup solutions, monitoring and managing power and cooling systems, developing and testing disaster recovery plans, training staff, conducting regular risk assessments, investing in advanced monitoring and analytics tools, and partnering with experienced data center providers, businesses can minimize downtime and achieve optimal performance in their data centers. It is essential for organizations to prioritize maximum uptime to avoid financial losses, reputational damage, and loss of customer trust. By implementing the best practices discussed in this blog post, businesses can ensure the reliability and availability of their data center operations.
If you’re interested in learning more about data center outage prevention, you might find this article on “Security is Paramount: Symantec Data Center Keeps You Safer Than Ever” quite informative. It discusses the importance of security measures in data centers and how Symantec’s data center solutions can help keep your data safe. Check it out here.
FAQs
What is a data center outage?
A data center outage is an unplanned interruption or failure in the operation of a data center, which can result in the loss of critical data, system downtime, and financial losses.
What are the causes of data center outages?
Data center outages can be caused by a variety of factors, including power failures, hardware failures, software bugs, human error, natural disasters, and cyber attacks.
What are the consequences of a data center outage?
The consequences of a data center outage can be severe, including lost revenue, damage to reputation, legal liabilities, and even business failure.
How can data center outages be prevented?
Data center outages can be prevented through a combination of measures, including redundancy, backup power systems, regular maintenance and testing, disaster recovery planning, and employee training.
What is redundancy in data centers?
Redundancy in data centers refers to the use of duplicate systems and components to ensure that if one fails, another can take over without interruption to the operation of the data center.
What is disaster recovery planning?
Disaster recovery planning is the process of creating a plan to recover critical systems and data in the event of a disaster or outage. This includes identifying potential risks, developing procedures for responding to them, and testing the plan regularly.
Why is employee training important in preventing data center outages?
Employee training is important in preventing data center outages because many outages are caused by human error. By providing employees with the knowledge and skills they need to operate and maintain data center systems properly, the risk of outages can be reduced.
In today’s digital age, data centers play a crucial role in supporting the growing demand for digital services and storage. These facilities are designed to house computer systems and associated components, such as telecommunications and storage systems. They provide a secure and controlled environment for the storage, management, and dissemination of data.
Data centers have become increasingly important as businesses and individuals rely on digital services for communication, entertainment, and productivity. With the exponential growth of data generated by various sources, including social media, IoT devices, and cloud computing, the need for data centers has skyrocketed.
Investing in data centers presents a unique opportunity for investors to capitalize on this growing demand. As more businesses and individuals require data storage and processing capabilities, the demand for data centers is expected to continue to rise. This article will explore the various aspects of data center investment opportunities, including market trends, key players, financial benefits, risks, technological advancements, and future growth prospects.
Key Takeaways
- Data center investment opportunities offer potential for high returns
- Understanding the data center market and demand is crucial for successful investment
- Key players in the industry include major tech companies and real estate investment trusts (REITs)
- Financial benefits of investing in data centers include steady cash flow and long-term leases
- Risks of data center investments include high upfront costs and potential for technological obsolescence
Understanding the Data Center Market
The global data center market has experienced significant growth in recent years and is expected to continue expanding at a rapid pace. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global data center market size was valued at $44.12 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $104.97 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 11.5% from 2021 to 2028.
The market can be segmented based on type, service, and end-user. In terms of type, there are two main categories: enterprise data centers and colocation data centers. Enterprise data centers are owned and operated by individual organizations to support their internal IT infrastructure needs. Colocation data centers, on the other hand, provide shared infrastructure and services to multiple customers.
In terms of services offered, data centers provide a range of solutions including storage, networking, security, and disaster recovery. The end-users of data centers include various industries such as IT and telecom, BFSI (banking, financial services, and insurance), healthcare, government, and others.
Key market trends driving the growth of the data center market include the increasing adoption of cloud computing, the rise of edge computing, the growing demand for colocation services, and the need for data security and compliance. These trends are fueled by factors such as the proliferation of digital services, the need for real-time data processing, and the increasing reliance on data-driven decision-making.
Analyzing the Demand for Data Centers
The demand for data centers is driven by several factors, including the increasing volume of data generated by businesses and individuals, the need for secure and reliable storage solutions, and the growing adoption of cloud computing.
In terms of regional demand, North America currently dominates the data center market due to its advanced IT infrastructure and high concentration of technology companies. However, Asia Pacific is expected to witness significant growth in the coming years due to factors such as rapid urbanization, increasing internet penetration, and government initiatives to promote digitalization.
In terms of industry demand, the IT and telecom sector is the largest consumer of data center services. This is followed by industries such as BFSI, healthcare, government, and others. The increasing digitization of these industries and their reliance on data-driven processes are driving the demand for data centers.
Future demand projections indicate that the demand for data centers will continue to grow as businesses and individuals generate more data and rely on digital services. Factors such as the increasing adoption of IoT devices, the expansion of 5G networks, and the rise of artificial intelligence are expected to further drive the demand for data center services.
Identifying Key Players in the Data Center Industry
| Key Players | Market Share | Revenue | Number of Data Centers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Equinix | 13.5% | 5.56 billion | 200+ |
| Digital Realty | 8.5% | 3.16 billion | 280+ |
| CyrusOne | 2.5% | 0.77 billion | 45+ |
| Global Switch | 2.0% | 0.70 billion | 10+ |
| NTT Communications | 1.5% | 0.60 billion | 140+ |
The data center industry is highly competitive, with several major players dominating the market. Some of the key players in this industry include Equinix, Digital Realty, NTT Communications, Microsoft, and Amazon Web Services (AWS).
Equinix is one of the largest data center providers globally, with a presence in over 50 markets worldwide. The company offers a range of services, including colocation, interconnection, and managed services. Equinix operates state-of-the-art data centers that provide high levels of security, reliability, and connectivity.
Digital Realty is another major player in the data center industry, with a global portfolio of data centers in key markets. The company offers a range of solutions, including colocation, interconnection, and cloud services. Digital Realty focuses on providing flexible and scalable data center solutions to meet the evolving needs of its customers.
NTT Communications is a leading global provider of ICT solutions and services, including data center services. The company operates a global network of data centers that provide secure and reliable infrastructure for businesses. NTT Communications offers a range of services, including colocation, cloud, and managed services.
Microsoft and Amazon Web Services (AWS) are two major players in the cloud computing market that also operate their own data centers. These companies offer a range of cloud services, including infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS). Their data centers provide the underlying infrastructure for their cloud services.
The competitive landscape of the data center industry is constantly evolving as new players enter the market and existing players expand their offerings. Market share analysis indicates that Equinix and Digital Realty are among the top players in terms of market share. However, the market is highly fragmented, with several regional and niche players catering to specific customer needs.
Key success factors for data center providers include the ability to offer reliable and secure infrastructure, provide high levels of connectivity and interconnection options, offer flexible and scalable solutions, and deliver excellent customer service. Data center providers that can differentiate themselves based on these factors are likely to gain a competitive advantage in the market.
Examining the Financial Benefits of Investing in Data Centers
Investing in data centers can provide several financial benefits for investors. Data centers generate revenue through various streams, including colocation services, cloud services, managed services, and interconnection services.
Colocation services involve renting physical space within a data center facility to house IT infrastructure. Customers pay a monthly fee based on the amount of space and power they require. This revenue stream provides a stable and predictable source of income for data center providers.
Cloud services involve providing virtualized infrastructure and software solutions to customers on a pay-as-you-go basis. This revenue model allows data center providers to generate revenue based on usage, providing scalability and flexibility for customers. Cloud services have become increasingly popular due to their cost-effectiveness and ease of use.
Managed services involve providing additional support and management services to customers, such as monitoring, maintenance, and security. These services can be offered as add-ons to colocation or cloud services, providing an additional revenue stream for data center providers.
Interconnection services involve facilitating direct connections between customers within a data center facility. This allows for faster and more secure data transfer between different networks and systems. Interconnection services can be offered as a standalone service or as part of a colocation or cloud service package.
Return on investment (ROI) analysis is an important factor to consider when evaluating data center investments. The ROI for data center investments can be calculated based on factors such as the initial investment cost, the expected revenue generated over a certain period, and the operational costs associated with running the facility.
Tax incentives and other financial benefits can also make data center investments more attractive. Many governments offer tax incentives, grants, or subsidies to attract data center investments to their regions. These incentives can include tax breaks on equipment purchases, reduced energy costs, or financial assistance for infrastructure development.
Evaluating the Risks of Data Center Investments


While data center investments offer significant financial benefits, they also come with certain risks that need to be carefully evaluated. These risks can be categorized into market and operational risks, regulatory and compliance risks, and disaster and security risks.
Market and operational risks include factors such as changes in market demand, competition, technological obsolescence, and operational inefficiencies. Data center investments require a long-term commitment, and changes in market dynamics or technological advancements can impact the profitability of the investment. Operational inefficiencies, such as downtime or service disruptions, can also result in financial losses.
Regulatory and compliance risks include factors such as changes in data protection laws, privacy regulations, and industry standards. Data centers are subject to various regulations and compliance requirements, which can vary by region and industry. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in fines, legal liabilities, or reputational damage.
Disaster and security risks include factors such as natural disasters, power outages, cyber-attacks, and physical breaches. Data centers are critical infrastructure that require robust security measures to protect against unauthorized access, data breaches, and other security threats. Natural disasters or power outages can also disrupt data center operations and result in financial losses.
To mitigate these risks, data center investors should conduct thorough due diligence before making an investment. This includes evaluating the market demand and competitive landscape, assessing the operational capabilities of the data center provider, conducting a risk assessment of the facility’s location, and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations and industry standards.
Assessing the Impact of Technology on Data Center Investments
The rapid advancement of technology has a significant impact on data center investments. Emerging technologies such as cloud computing, edge computing, artificial intelligence (AI), and automation are reshaping the data center landscape.
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses store and process data. It allows businesses to access computing resources on-demand without the need for physical infrastructure. This has led to the rise of cloud service providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform. Data center investments are closely tied to the growth of cloud computing, as these providers rely on data centers to host their infrastructure.
Edge computing is another emerging technology that is driving the demand for data centers. Edge computing involves processing data closer to the source, reducing latency and improving real-time data processing capabilities. This requires data centers to be located closer to end-users, resulting in the need for smaller, distributed data centers.
Artificial intelligence and automation are also transforming data center operations. AI can be used to optimize energy consumption, improve security, and automate routine tasks. Automation technologies such as robotic process automation (RPA) and software-defined networking (SDN) are also being adopted to streamline data center operations and improve efficiency.
These technological advancements have both positive and negative implications for data center investments. On one hand, they drive the demand for data center services as businesses and individuals require more storage and processing capabilities. On the other hand, they also pose challenges for data center providers in terms of infrastructure scalability, energy efficiency, and security.
Exploring the Future of Data Center Investments
The future of data center investments looks promising, with several market trends and growth opportunities on the horizon. The increasing adoption of emerging technologies such as IoT, 5G, AI, and blockchain is expected to drive the demand for data center services.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of interconnected devices that collect and exchange data. The proliferation of IoT devices is generating massive amounts of data that need to be processed and stored in data centers. This trend is expected to continue as more industries adopt IoT technologies.
The rollout of 5G networks is also expected to drive the demand for data center services. 5G networks require low-latency and high-bandwidth connections, which can be provided by data centers located closer to end-users. This will result in the need for more edge data centers to support the growing demand for 5G services.
Artificial intelligence is another technology that is expected to have a significant impact on data center investments. AI requires large amounts of computing power and storage, which can be provided by data centers. As AI applications become more widespread, the demand for data center services is expected to increase.
Blockchain technology is also driving the demand for data center services, particularly in the cryptocurrency industry. Blockchain networks require secure and reliable infrastructure to store and process transactions. Data centers provide the necessary infrastructure to support blockchain networks, making them an essential component of the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
While the future of data center investments looks promising, there are also potential challenges and risks that need to be considered. These include factors such as increasing competition, evolving customer demands, regulatory changes, and technological disruptions. Data center investors need to stay informed about market trends and developments to capitalize on future growth opportunities.
Strategies for Maximizing Profit from Data Center Investments
To maximize profit from data center investments, investors should consider implementing strategies such as portfolio diversification, operational efficiency, and innovation.
Portfolio diversification involves investing in a mix of different types of data centers, such as enterprise data centers and colocation data centers. This helps spread the risk and ensures a steady stream of income from different sources. Diversification can also involve investing in data centers located in different regions or industries to capture different market opportunities.
Operational efficiency is another key factor in maximizing profit from data center investments. This includes optimizing energy consumption, reducing downtime, improving maintenance processes, and implementing automation technologies. By improving operational efficiency, data center providers can reduce costs and improve profitability.
Innovation and differentiation are also important strategies for maximizing profit from data center investments. Data center providers should continuously innovate their services and offerings to stay ahead of the competition. This can involve developing new solutions, improving security measures, or adopting emerging technologies. By differentiating themselves from competitors, data center providers can attract more customers and command higher prices.
Unlocking Profit through Data Center Investment Opportunities
In conclusion, data center investments present a unique opportunity for investors to capitalize on the growing demand for digital services and storage. Data centers play a crucial role in supporting the digital economy by providing secure and reliable infrastructure for data storage and processing.
The global data center market is experiencing significant growth, driven by factors such as the increasing adoption of cloud computing, the rise of edge computing, and the growing demand for colocation services. Data center investments offer several financial benefits, including stable revenue streams, attractive ROI potential, and tax incentives.
However, data center investments also come with certain risks that need to be carefully evaluated and mitigated. These risks include market and operational risks, regulatory and compliance risks, and disaster and security risks. Thorough due diligence and risk assessment are essential before making an investment.
The future of data center investments looks promising, with several market trends and growth opportunities on the horizon. Emerging technologies such as IoT, 5G, AI, and blockchain are expected to drive the demand for data center services. To maximize profit from data center investments, investors should consider implementing strategies such as portfolio diversification, operational efficiency, and innovation.
In conclusion, data center investments offer a lucrative opportunity for investors to unlock profit in the digital economy. As businesses and individuals continue to rely on digital services and generate more data, the demand for data centers will only increase. This growing demand, coupled with the potential for long-term contracts and recurring revenue streams, makes data center investments an attractive option for investors. Additionally, the stability and resilience of data centers, along with their ability to adapt to changing technology trends, provide a sense of security for investors. Furthermore, the global nature of data center investments allows for diversification and the potential to tap into emerging markets. Overall, data center investments present a promising avenue for investors to capitalize on the ever-expanding digital landscape and reap substantial financial rewards.
If you’re interested in exploring the cutting-edge technologies and transformative impact on the data center industry’s future, you won’t want to miss this article on AI-powered data centers. Discover how artificial intelligence is revolutionizing data center operations and optimizing efficiency. From predictive maintenance to intelligent resource allocation, AI is reshaping the way data centers operate. To learn more about this exciting topic, check out this article.
FAQs
What are data centers?
Data centers are facilities that house computer systems and associated components, such as telecommunications and storage systems. They are used to store, process, and manage large amounts of data.
Why are data centers important?
Data centers are important because they enable businesses and organizations to store and process large amounts of data, which is essential for their operations. They also provide a secure and reliable environment for data storage and processing.
What are the investment opportunities in data centers?
Investment opportunities in data centers include investing in the construction and operation of data centers, as well as investing in companies that provide data center services, such as cloud computing and colocation services.
What are the benefits of investing in data centers?
Investing in data centers can provide a number of benefits, including potential for high returns on investment, long-term revenue streams, and exposure to a growing industry.
What are the risks associated with investing in data centers?
Risks associated with investing in data centers include changes in technology that could make data centers obsolete, changes in regulations that could impact the industry, and competition from other data center providers.
What should investors consider before investing in data centers?
Investors should consider factors such as the location of the data center, the demand for data center services in the area, the reputation of the data center provider, and the financial stability of the provider before investing in data centers.
Smart technologies in data centers refer to the use of advanced technologies and systems to optimize the efficiency, reliability, and security of data centers. These technologies include artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, internet of things (IoT), virtualization, cloud computing, blockchain, and green technologies. The implementation of smart technologies in data centers is becoming increasingly important as the demand for data storage and processing continues to grow.
The importance of smart technologies in data centers cannot be overstated. With the exponential growth of data and the increasing reliance on digital infrastructure, data centers play a critical role in supporting various industries and services. Smart technologies enable data centers to operate more efficiently, reduce costs, improve reliability and uptime, enhance security, and promote sustainability. By leveraging these technologies, data centers can meet the ever-increasing demands of the digital age.
Key Takeaways
- Smart technologies are transforming data centers to be more efficient and sustainable.
- Revolutionizing data centers is necessary to keep up with the increasing demand for data processing and storage.
- Smart technologies bring benefits such as improved energy efficiency, reduced downtime, and cost savings.
- Smart sensors enable precise temperature control, which is crucial for maintaining optimal conditions for equipment.
- AI and machine learning can predict maintenance needs, reducing the risk of equipment failure and downtime.
The Need for Revolutionizing Data Centers
Traditional data centers face numerous challenges that necessitate a revolution in their operations. These challenges include increasing energy consumption, rising costs, limited scalability, lack of real-time monitoring and control, and concerns about data security and transparency. In order to address these challenges and meet the growing demands of the digital economy, data centers need to embrace smart technologies.
The need for revolutionizing data centers is driven by the need for increased efficiency, reliability, and security. Traditional data centers are often inefficient in terms of energy consumption and resource utilization. They rely on manual processes and outdated systems that are prone to errors and downtime. By adopting smart technologies, data centers can optimize their operations, reduce energy consumption, and improve overall efficiency.
Benefits of Smart Technologies in Data Centers
The adoption of smart technologies in data centers brings a multitude of benefits. These benefits include increased efficiency and productivity, cost savings, improved reliability and uptime, and enhanced security.
Increased efficiency and productivity: Smart technologies enable data centers to automate processes, optimize resource allocation, and improve overall efficiency. This leads to increased productivity and faster response times. For example, AI and machine learning algorithms can analyze data in real-time and make intelligent decisions to optimize workloads and allocate resources more effectively.
Cost savings: By improving efficiency and reducing energy consumption, smart technologies can help data centers save costs. Virtualization and cloud computing, for example, allow data centers to consolidate servers and reduce hardware costs. AI and machine learning can also help optimize energy usage and reduce operational expenses.
Improved reliability and uptime: Smart technologies enable data centers to proactively monitor and manage their infrastructure, leading to improved reliability and uptime. Predictive maintenance using AI and machine learning algorithms can detect potential issues before they cause downtime, allowing for timely repairs or replacements.
Enhanced security: Data security is a top priority for data centers. Smart technologies such as blockchain can provide enhanced security and transparency by creating an immutable record of transactions and ensuring data integrity. IoT devices can also be used for real-time monitoring and control, detecting any unauthorized access or anomalies.
Smart Sensors for Efficient Temperature Control
| Smart Sensors for Efficient Temperature Control | Metrics |
|---|---|
| Energy Savings | Up to 30% |
| Accuracy | ±0.5°C |
| Response Time | Less than 5 seconds |
| Connectivity | Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee |
| Compatibility | Works with most HVAC systems |
| Installation | Easy and quick |
| Cost | Affordable |
Temperature control is crucial in data centers as it directly affects the performance and lifespan of the equipment. Smart sensors play a vital role in improving temperature control by providing real-time monitoring and control.
Maintaining the optimal temperature in a data center is essential to prevent overheating and equipment failure. Smart sensors can continuously monitor temperature levels throughout the facility and alert operators if there are any deviations from the desired range. This allows for timely adjustments to be made to ensure that the temperature remains within the optimal range.
Smart sensors can also enable dynamic temperature control by adjusting cooling systems based on real-time data. For example, if a particular area of the data center is experiencing higher heat loads, smart sensors can detect this and increase cooling in that specific area. This ensures that cooling resources are allocated efficiently, reducing energy consumption and costs.
Examples of smart sensors for temperature control include thermal imaging cameras, temperature sensors, and humidity sensors. These sensors can be integrated into the data center’s infrastructure and connected to a central monitoring system for real-time data analysis and control.
AI and Machine Learning for Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance is crucial in data centers to prevent equipment failures and minimize downtime. AI and machine learning algorithms can greatly improve predictive maintenance by analyzing large amounts of data and identifying patterns that indicate potential issues.
Traditional maintenance practices in data centers are often reactive, meaning that repairs or replacements are made after a failure has occurred. This approach can lead to costly downtime and reduced productivity. By implementing predictive maintenance using AI and machine learning, data centers can detect potential issues before they cause failures.
AI and machine learning algorithms can analyze data from various sources, such as equipment sensors, performance logs, and historical maintenance records. By identifying patterns and anomalies in the data, these algorithms can predict when a piece of equipment is likely to fail. This allows for proactive maintenance to be scheduled, minimizing downtime and reducing costs.
Examples of AI and machine learning in data centers include anomaly detection algorithms, predictive analytics models, and condition-based monitoring systems. These technologies can be integrated into the data center’s infrastructure to continuously monitor equipment health and provide real-time insights for maintenance planning.
Virtualization and Cloud Computing for Scalability


Scalability is a critical factor in data centers as they need to accommodate the increasing demands for storage and processing power. Virtualization and cloud computing technologies offer scalable solutions that allow data centers to expand their capacity as needed.
Virtualization involves creating virtual instances of servers, storage devices, and networks. This allows multiple virtual machines to run on a single physical server, maximizing resource utilization. Virtualization also enables the easy migration of virtual machines between physical servers, providing flexibility and scalability.
Cloud computing takes virtualization a step further by providing on-demand access to computing resources over the internet. Data centers can leverage cloud computing services to scale their infrastructure up or down based on demand. This eliminates the need for upfront investments in hardware and allows for more efficient resource allocation.
Examples of virtualization and cloud computing in data centers include hypervisors, virtual machine managers, and cloud service providers. These technologies enable data centers to scale their operations quickly and efficiently, ensuring that they can meet the growing demands of the digital economy.
Blockchain for Data Security and Transparency
Data security and transparency are critical in data centers as they handle sensitive information from various sources. Blockchain technology offers a decentralized and secure solution for data storage and transaction verification.
Blockchain is a distributed ledger that records transactions across multiple nodes in a network. Each transaction is encrypted and linked to the previous transaction, creating an immutable chain of records. This ensures that data cannot be altered or tampered with, providing a high level of security and integrity.
In data centers, blockchain can be used to securely store sensitive information such as user credentials, transaction logs, and audit trails. By decentralizing data storage, blockchain reduces the risk of a single point of failure or unauthorized access. It also provides transparency as all transactions are recorded on the blockchain and can be audited by authorized parties.
Examples of blockchain in data centers include secure identity management systems, supply chain tracking platforms, and decentralized storage solutions. These applications leverage blockchain’s security and transparency features to ensure the integrity of data stored in data centers.
IoT for Real-time Monitoring and Control
Real-time monitoring and control are essential in data centers to ensure optimal performance and prevent downtime. IoT devices can provide real-time insights into various aspects of the data center’s infrastructure, enabling operators to make informed decisions quickly.
IoT devices such as sensors, cameras, and actuators can be deployed throughout the data center to monitor temperature, humidity, power consumption, airflow, and other parameters. These devices collect data in real-time and transmit it to a central monitoring system for analysis.
By analyzing the data from IoT devices, data center operators can identify potential issues or anomalies and take immediate action. For example, if a sensor detects a sudden increase in temperature in a specific area, operators can investigate the cause and make adjustments to prevent equipment failure.
Examples of IoT in data centers include environmental monitoring systems, asset tracking solutions, and energy management platforms. These applications leverage IoT devices to provide real-time insights into the data center’s operations, enabling proactive monitoring and control.
Green Technologies for Sustainable Data Centers
Sustainability is becoming increasingly important in data centers as the demand for energy continues to rise. Green technologies offer solutions to reduce energy consumption, minimize carbon footprint, and promote sustainability in data centers.
Data centers are known for their high energy consumption due to the constant operation of servers, cooling systems, and other infrastructure. Green technologies such as energy-efficient hardware, renewable energy sources, and advanced cooling systems can help reduce energy consumption and carbon emissions.
Energy-efficient hardware includes servers, storage devices, and networking equipment that are designed to consume less power while maintaining high performance. Renewable energy sources such as solar panels and wind turbines can be used to generate clean energy for data centers. Advanced cooling systems such as liquid cooling or free cooling can reduce the energy required for cooling the data center.
Examples of green technologies in data centers include server virtualization, power management software, renewable energy installations, and advanced cooling systems. These technologies enable data centers to operate more sustainably and reduce their environmental impact.
Challenges and Future of Smart Technologies in Data Centers
While smart technologies offer numerous benefits for data centers, they also face several challenges that need to be addressed. These challenges include high implementation costs, complexity of integration, lack of skilled personnel, and concerns about data privacy.
The implementation costs of smart technologies can be significant, especially for smaller data centers with limited budgets. The complexity of integrating different technologies and systems can also pose challenges, requiring expertise and resources.
Furthermore, the adoption of smart technologies requires skilled personnel who can manage and operate these technologies effectively. There is a shortage of skilled professionals in the field of data center management and smart technologies, which can hinder the widespread adoption of these technologies.
Data privacy is another concern when it comes to smart technologies in data centers. With the increasing amount of data being collected and analyzed, there is a need to ensure that data is protected and used responsibly. Data centers need to implement robust security measures and comply with privacy regulations to address these concerns.
Despite these challenges, the future of smart technologies in data centers looks promising. As technology continues to advance, the costs of implementation are expected to decrease, making smart technologies more accessible to a wider range of data centers. The integration of different technologies will also become more seamless, allowing for easier adoption and management.
In terms of future trends and developments, we can expect to see further advancements in AI and machine learning algorithms for predictive maintenance, as well as the use of edge computing for real-time processing and analysis. The adoption of renewable energy sources and energy-efficient hardware will also continue to grow, promoting sustainability in data centers.
In conclusion, smart technologies have revolutionized data centers by improving efficiency, reducing costs, enhancing reliability and security, and promoting sustainability. From smart sensors for temperature control to AI and machine learning for predictive maintenance, these technologies offer numerous benefits for data centers. While there are challenges to overcome, the future of smart technologies in data centers looks promising as technology continues to advance. Data centers that embrace these technologies will be better equipped to meet the growing demands of the digital economy.
If you’re interested in learning more about the importance of data center security and how to protect against cyber attacks, check out this informative article on DataCenterInfo.com. It provides valuable tips and insights on creating a secure and HIPAA-compliant data center. With the increasing threat of cyber attacks, it is crucial for businesses to implement robust security measures to safeguard their sensitive data. This article offers practical advice and best practices to help organizations strengthen their data center security. Read more
FAQs
What are smart data center technologies?
Smart data center technologies refer to the use of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT) to optimize the performance, efficiency, and security of data centers.
What are the benefits of smart data center technologies?
Smart data center technologies offer several benefits, including improved energy efficiency, reduced operational costs, enhanced security, increased reliability, and better performance.
How do smart data center technologies improve energy efficiency?
Smart data center technologies improve energy efficiency by using advanced cooling systems, optimizing server utilization, and implementing power management techniques such as dynamic voltage and frequency scaling.
What is the role of artificial intelligence in smart data center technologies?
Artificial intelligence plays a crucial role in smart data center technologies by enabling predictive maintenance, automating routine tasks, and optimizing resource allocation.
What is the Internet of Things (IoT) in the context of smart data center technologies?
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of physical devices, sensors, and other objects that are connected to the internet and can exchange data. In the context of smart data center technologies, IoT devices can be used to monitor and control various aspects of the data center environment, such as temperature, humidity, and power consumption.
What are some examples of smart data center technologies?
Some examples of smart data center technologies include virtualization, software-defined networking, edge computing, predictive analytics, and automation tools.
Data centers play a crucial role in modern business operations. They are the backbone of the digital infrastructure that supports organizations in storing, processing, and managing vast amounts of data. With the increasing reliance on technology and the growing importance of data-driven decision making, the uptime of data centers has become a critical factor for businesses. Uptime refers to the amount of time that a data center is operational and available for use. In this article, we will explore the importance of uptime in data centers and discuss the key components of data center maintenance services that ensure optimal uptime.
Key Takeaways
- Uptime is crucial for data centers to ensure uninterrupted operations and avoid costly downtime.
- Key components of data center maintenance services include power management, cooling and HVAC maintenance, network and connectivity maintenance, and security and surveillance maintenance.
- Preventive maintenance strategies such as regular equipment inspections and upgrades can help optimize uptime.
- Data center cooling and HVAC maintenance best practices include monitoring temperature and humidity levels, cleaning air filters, and checking for leaks.
- Partnering with expert data center maintenance providers can help ensure maximum uptime and minimize the risk of downtime.
Understanding the Importance of Uptime in Data Centers
Uptime is a fundamental metric for data centers as it directly impacts business operations. When a data center experiences downtime, it means that it is not accessible or functioning properly. This can have severe consequences for businesses, including loss of productivity, revenue, and customer trust. In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, downtime can result in significant financial losses and damage to a company’s reputation.
The impact of downtime on business operations can be far-reaching. It can disrupt critical processes such as online transactions, customer support systems, and communication channels. For example, an e-commerce website that experiences downtime during peak shopping seasons may lose out on potential sales and damage customer loyalty. Similarly, a financial institution that relies on real-time data processing may face severe consequences if its data center goes offline.
The financial implications of downtime can be staggering. According to a study by the Ponemon Institute, the average cost of data center downtime is $9,000 per minute. This includes direct costs such as lost revenue and increased expenses for recovery efforts, as well as indirect costs such as damage to brand reputation and customer trust. For businesses that rely heavily on their data centers, even a few minutes of downtime can result in significant financial losses.
Key Components of Data Center Maintenance Services
To ensure optimal uptime, data center maintenance services encompass various components that work together to keep the data center running smoothly. These components include preventive maintenance, regular equipment inspections and upgrades, cooling and HVAC maintenance, power management and backup solutions, network and connectivity maintenance, security and surveillance maintenance, and disaster recovery planning.
Preventive maintenance is a proactive approach to data center maintenance that involves regularly scheduled inspections, testing, and servicing of equipment. This helps identify and address potential issues before they escalate into major problems. Preventive maintenance includes tasks such as cleaning equipment, checking for loose connections, and replacing worn-out parts. By implementing preventive maintenance strategies, data centers can minimize the risk of unexpected downtime and ensure the continuous operation of critical systems.
Regular equipment inspections and upgrades are essential for maintaining the efficiency and reliability of data center infrastructure. As technology evolves rapidly, outdated equipment can become a bottleneck for data center operations. Regular inspections help identify equipment that is nearing the end of its lifespan or is no longer capable of meeting the demands of the business. Upgrading to newer, more efficient equipment can improve performance, reduce energy consumption, and enhance overall uptime.
Data center cooling and HVAC maintenance is crucial for ensuring optimal uptime. Data centers generate a significant amount of heat due to the constant operation of servers and other equipment. If not properly managed, this heat can lead to equipment failure and downtime. Cooling systems must be regularly inspected, cleaned, and maintained to ensure they are functioning at their best capacity. HVAC systems should also be monitored to maintain proper temperature and humidity levels within the data center.
Power management and backup solutions are essential for maintaining uptime in data centers. Power outages can occur due to various reasons such as natural disasters, utility failures, or equipment malfunctions. Data centers must have robust power management systems in place to ensure uninterrupted power supply. This includes backup generators, uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems, and redundant power distribution units (PDUs). These solutions provide a reliable power source during outages and prevent data loss or system failures.
Network and connectivity maintenance is critical for ensuring reliable performance in data centers. Networks are the lifeline of data centers, connecting servers, storage devices, and other equipment. Regular maintenance of network infrastructure helps identify and resolve issues such as network congestion, latency, or security vulnerabilities. It also involves monitoring network traffic, optimizing bandwidth usage, and implementing security measures to protect against cyber threats.
Security and surveillance maintenance is essential for protecting data centers from physical and cyber threats. Data centers house valuable and sensitive information, making them attractive targets for hackers and criminals. Regular maintenance of security systems such as access control, surveillance cameras, and fire detection systems helps ensure the physical security of the data center. Additionally, regular updates and patches to software and firmware protect against cyber threats such as malware, viruses, and unauthorized access.
Disaster recovery planning and maintenance are crucial for ensuring business continuity in the event of a catastrophic event. Data centers must have comprehensive disaster recovery plans in place to minimize downtime and data loss in case of natural disasters, power outages, or other emergencies. This includes regular testing of backup systems, off-site data replication, and documentation of recovery procedures. By having a robust disaster recovery plan, data centers can quickly recover from disruptions and resume normal operations.
Partnering with Expert Data Center Maintenance Providers for Maximum Uptime
| Metrics | Description |
|---|---|
| Uptime | The percentage of time that a data center is operational and available for use. |
| Downtime | The amount of time that a data center is not operational and unavailable for use. |
| SLA | Service Level Agreement, a contract between a data center provider and a customer that outlines the level of service that will be provided. |
| Maintenance | The process of keeping a data center’s equipment and infrastructure in good working order to prevent downtime. |
| Expertise | The level of knowledge and experience that a data center maintenance provider has in maintaining and repairing data center equipment. |
| Cost | The amount of money that a data center maintenance provider charges for their services. |
Maintaining optimal uptime in data centers requires specialized knowledge and expertise. Many businesses choose to partner with expert data center maintenance providers to ensure their data centers are operating at peak performance. These providers offer a range of services including preventive maintenance, equipment inspections and upgrades, cooling and HVAC maintenance, power management solutions, network and connectivity maintenance, security and surveillance maintenance, and disaster recovery planning.
By outsourcing data center maintenance services to experts, businesses can benefit from their extensive experience and knowledge in managing complex data center environments. These providers have dedicated teams of technicians who are trained to identify and resolve issues quickly and efficiently. They also have access to the latest tools, technologies, and best practices in data center maintenance.
Outsourcing data center maintenance services can also provide cost savings for businesses. Instead of investing in expensive equipment, training, and resources to maintain their data centers in-house, businesses can leverage the expertise of maintenance providers at a fraction of the cost. Additionally, outsourcing allows businesses to focus on their core competencies and strategic initiatives, while leaving the maintenance of their data centers in the hands of professionals.
In today’s digital age, data centers are the backbone of modern business operations. The uptime of data centers is crucial for ensuring uninterrupted access to critical systems and applications. Downtime can have severe consequences for businesses, including loss of productivity, revenue, and customer trust. To ensure optimal uptime, businesses must prioritize data center maintenance.
Data center maintenance services encompass various components such as preventive maintenance, regular equipment inspections and upgrades, cooling and HVAC maintenance, power management and backup solutions, network and connectivity maintenance, security and surveillance maintenance, and disaster recovery planning. These components work together to keep data centers running smoothly and minimize the risk of downtime.
Partnering with expert data center maintenance providers can help businesses ensure maximum uptime. These providers offer a range of services and have the knowledge and expertise to manage complex data center environments. By outsourcing data center maintenance services, businesses can benefit from cost savings, specialized expertise, and the ability to focus on their core competencies. Prioritizing data center maintenance is essential for businesses to thrive in today’s digital landscape.
If you’re interested in data center maintenance services, you may also want to check out this informative article on creating a secure and HIPAA-compliant data center. It provides valuable tips for ensuring the security and compliance of your data center environment. To learn more, click here.
FAQs
What are data center maintenance services?
Data center maintenance services refer to the activities carried out to ensure the smooth operation of a data center. These services include regular inspections, repairs, upgrades, and replacements of equipment and infrastructure.
Why are data center maintenance services important?
Data center maintenance services are important because they help to prevent downtime, ensure data security, and extend the lifespan of equipment. Regular maintenance also helps to identify potential issues before they become major problems.
What types of equipment are included in data center maintenance services?
Data center maintenance services typically include maintenance of servers, storage devices, networking equipment, cooling systems, power systems, and security systems.
Who provides data center maintenance services?
Data center maintenance services can be provided by the data center owner or by a third-party maintenance provider. Third-party maintenance providers specialize in data center maintenance and can provide more comprehensive services than in-house teams.
What are the benefits of outsourcing data center maintenance services?
Outsourcing data center maintenance services can provide several benefits, including cost savings, access to specialized expertise, increased efficiency, and reduced downtime. Third-party maintenance providers can also provide customized maintenance plans to meet the specific needs of a data center.
How often should data center maintenance services be performed?
The frequency of data center maintenance services depends on several factors, including the age of equipment, the level of usage, and the manufacturer’s recommendations. Generally, maintenance services should be performed at least once a year, but more frequent maintenance may be necessary for older or heavily used equipment.
Data centers are centralized locations where organizations store, manage, and process large amounts of data. They are the backbone of today’s digital world, supporting everything from cloud computing to online shopping and social media. As technology continues to advance at a rapid pace, data centers are also evolving to meet the growing demands of the digital age.
In recent years, there have been significant advancements and innovations in data center technology. These advancements have focused on improving efficiency, reducing costs, enhancing security, and increasing scalability. From the emergence of edge computing to the implementation of artificial intelligence and machine learning, data centers are undergoing a transformation that will shape the future of technology.
Key Takeaways
- Data centers are becoming increasingly important in today’s digital world.
- Edge computing is emerging as a new trend that is impacting data centers.
- Advances in cooling systems are improving efficiency and reducing costs in data centers.
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning are playing a key role in data center management.
- Modular data centers offer benefits but also come with challenges.
The Growing Importance of Data Centers in Today’s Digital World
Data centers play a crucial role in supporting digital transformation. As businesses increasingly rely on technology to operate and compete in the global marketplace, the demand for data storage and processing has skyrocketed. From storing customer data to running complex algorithms for machine learning, data centers are essential for businesses to thrive in the digital age.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further highlighted the importance of data centers. With more people working remotely and relying on online services, the demand for data center resources has surged. From video conferencing platforms to e-commerce websites, these services require robust data center infrastructure to handle the increased traffic and ensure a seamless user experience.
The Emergence of Edge Computing and Its Impact on Data Centers
Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the source of data generation. Unlike traditional centralized data centers, edge computing allows for real-time processing and analysis of data at or near the edge devices. This reduces latency and bandwidth usage while enabling faster decision-making.
The rise of edge computing is changing the data center landscape. Instead of relying solely on large centralized data centers, organizations are now deploying smaller edge data centers closer to the end-users. This allows for faster data processing and reduces the need to transmit large amounts of data back and forth between the edge devices and the centralized data centers.
While edge computing offers many benefits, it also presents challenges for data centers. Managing a distributed network of edge data centers requires robust connectivity, security, and monitoring systems. Additionally, organizations need to carefully balance the workload between edge and centralized data centers to ensure optimal performance and resource utilization.
Advances in Data Center Cooling Systems: Improving Efficiency and Reducing Costs
| Metrics | Description |
|---|---|
| Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) | A metric used to determine the energy efficiency of a data center by dividing the total amount of energy used by the IT equipment by the total energy used by the entire facility. |
| Cooling Capacity | The amount of heat that can be removed from a data center by the cooling system. |
| Chilled Water Temperature | The temperature of the water used in the cooling system to remove heat from the data center. |
| Airflow Management | The practice of optimizing the flow of air through a data center to improve cooling efficiency and reduce energy consumption. |
| Free Cooling | The use of outside air to cool a data center instead of relying solely on mechanical cooling systems. |
| Heat Recovery | The process of capturing waste heat from a data center and using it to heat other areas of the facility. |
| Renewable Energy | The use of sustainable energy sources such as solar or wind power to reduce the carbon footprint of a data center. |
Cooling systems are a critical component of data centers as they help maintain optimal operating temperatures for the servers and other equipment. However, traditional cooling methods can be energy-intensive and costly. As data centers continue to grow in size and power density, there is a need for more efficient cooling solutions.
Over the years, there have been significant advancements in data center cooling technology. From hot aisle/cold aisle containment to liquid cooling solutions, these innovations have improved energy efficiency and reduced costs. For example, liquid cooling systems can remove heat more efficiently than air-based systems, resulting in lower energy consumption and reduced carbon footprint.
The latest advancements in data center cooling technology include the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms to optimize cooling operations. These algorithms can analyze real-time data from sensors and adjust cooling parameters accordingly, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently and cooling is delivered where it is needed the most.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Data Center Management
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are revolutionizing data center management. AI refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think and learn like humans, while ML is a subset of AI that focuses on algorithms that can learn from and make predictions or decisions based on data.
AI and ML are transforming data center management by automating routine tasks, optimizing resource allocation, and improving overall efficiency. For example, AI-powered predictive analytics can analyze historical data to forecast future demand and adjust resource allocation accordingly. This helps data centers optimize their operations, reduce downtime, and improve energy efficiency.
However, there are also challenges associated with using AI and ML in data centers. One of the main challenges is the need for large amounts of high-quality data to train the algorithms. Data centers need to ensure that they have access to clean and relevant data to achieve accurate predictions and decisions. Additionally, there are concerns about the ethical implications of AI and ML in data center management, such as bias in decision-making algorithms.
The Rise of Modular Data Centers: Benefits and Challenges


Modular data centers are pre-fabricated units that can be quickly deployed and easily scaled to meet the changing needs of organizations. These modular units contain all the necessary components of a traditional data center, including servers, storage, cooling systems, and power distribution.
The benefits of modular data centers include faster deployment times, lower upfront costs, and increased flexibility. Organizations can quickly add or remove modules as their needs change, allowing for more efficient resource allocation. Additionally, modular data centers are often designed with energy efficiency in mind, reducing operational costs and environmental impact.
However, there are challenges associated with implementing modular data centers. One challenge is the need for careful planning and coordination to ensure that the modules are properly integrated into the existing infrastructure. Additionally, organizations need to consider factors such as connectivity, security, and maintenance when deploying modular data centers.
The Impact of 5G Technology on Data Center Infrastructure and Design
5G technology is the next generation of wireless communication that promises faster speeds, lower latency, and increased capacity. This technology is expected to have a significant impact on data center infrastructure and design.
With 5G technology, more devices will be connected to the internet, generating massive amounts of data that need to be processed and stored. This will require data centers to have the capacity to handle the increased traffic and provide low-latency services. Additionally, the distributed nature of 5G networks may require data centers to be located closer to the edge devices to reduce latency and improve performance.
However, there are also challenges associated with 5G technology for data centers. The increased demand for data storage and processing may put a strain on existing data center infrastructure, requiring organizations to invest in upgrading their facilities. Additionally, the implementation of 5G technology may require changes in data center design to accommodate the increased power and cooling requirements.
The Future of Data Center Security: Addressing Emerging Threats and Risks
Data center security is of utmost importance as organizations store and process sensitive data. With the increasing sophistication of cyber threats, data centers need to constantly evolve their security measures to protect against emerging risks.
Emerging threats to data center security include ransomware attacks, insider threats, and supply chain vulnerabilities. Ransomware attacks involve encrypting data and demanding a ransom for its release, while insider threats involve malicious actions by employees or contractors with access to sensitive information. Supply chain vulnerabilities refer to the risks associated with third-party vendors and suppliers.
To address these emerging threats, data centers are implementing advanced security technologies such as biometric authentication, encryption, and intrusion detection systems. Additionally, organizations are investing in employee training and awareness programs to mitigate the risk of insider threats. Collaboration between data center operators, cybersecurity experts, and law enforcement agencies is also crucial in combating cybercrime.
The Growing Trend of Green Data Centers: Environmental Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Environmental sustainability and energy efficiency are becoming increasingly important considerations for data centers. As these facilities consume massive amounts of energy, there is a growing need to reduce their carbon footprint and minimize their impact on the environment.
Green data centers focus on implementing energy-efficient technologies and practices to reduce energy consumption and waste. This includes using energy-efficient servers, optimizing cooling systems, and implementing renewable energy sources such as solar or wind power. Additionally, data centers are adopting measures to recycle or reuse waste heat generated by the servers.
The benefits of implementing green data centers include reduced operational costs, improved brand reputation, and compliance with environmental regulations. However, there are also challenges associated with implementing green data centers, such as the high upfront costs of upgrading infrastructure and the need for ongoing monitoring and maintenance to ensure optimal energy efficiency.
The Importance of Collaboration and Partnerships in Driving Innovation in Data Centers
Collaboration and partnerships play a crucial role in driving innovation in data centers. The complexity and scale of data center operations require expertise from various stakeholders, including technology vendors, service providers, and industry organizations.
Collaboration between data center operators and technology vendors can lead to the development of innovative solutions that address specific challenges or requirements. For example, a collaboration between a data center operator and a cooling system manufacturer can result in the development of a more efficient cooling solution that reduces energy consumption and costs.
Partnerships between data center operators and service providers can also drive innovation by leveraging each other’s strengths. For example, a partnership between a data center operator and a cloud service provider can result in the development of hybrid cloud solutions that combine the scalability of the cloud with the security and control of an on-premises data center.
In conclusion, the future of data centers is filled with innovations and advancements that will shape the way we store, manage, and process data. From edge computing to AI-powered management systems, these advancements are driven by the increasing demand for data storage and processing in today’s digital world. As technology continues to evolve, collaboration and partnerships will play a crucial role in driving innovation in data centers. By working together, stakeholders can develop solutions that address the challenges and opportunities of the future.
If you’re interested in the future of data centers, you may also want to check out this informative article on datacenterinfo.com. It discusses the importance of securing information with data center security best practices, both in terms of physical and digital measures. With cyber threats becoming increasingly sophisticated, it is crucial for data centers to implement robust security measures to protect sensitive data. This article provides valuable insights and recommendations for ensuring the safety and integrity of your data. Read more
FAQs
What is a data center?
A data center is a facility used to house computer systems and associated components, such as telecommunications and storage systems.
What is the future of data centers?
The future of data centers is expected to be more efficient, sustainable, and flexible. This includes the use of renewable energy sources, modular designs, and advanced cooling technologies.
What are the benefits of modular data centers?
Modular data centers offer several benefits, including faster deployment times, scalability, and reduced costs. They also allow for easier maintenance and upgrades.
What is edge computing?
Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the location where it is needed, improving response times and reducing bandwidth usage.
What are the challenges facing data centers?
Some of the challenges facing data centers include energy consumption, cooling requirements, and security concerns. Additionally, the increasing demand for data storage and processing is putting pressure on data centers to keep up with the pace of technological advancements.
What is the role of artificial intelligence in data centers?
Artificial intelligence can be used in data centers to optimize energy usage, improve cooling efficiency, and automate maintenance tasks. It can also be used to analyze data and provide insights that can help improve overall performance.
Data centers are facilities that house computer systems and associated components, such as telecommunications and storage systems. They play a crucial role in modern society, as they are responsible for storing, processing, and transmitting vast amounts of data. From social media platforms to e-commerce websites, data centers are the backbone of the digital age.
However, the rapid growth of data centers has raised concerns about their environmental impact. These facilities consume enormous amounts of energy, emit greenhouse gases, and have a significant impact on air quality, water resources, land use, biodiversity, and e-waste. It is essential to understand and address these environmental issues to ensure a sustainable future for data centers.
Key Takeaways
- Data centers have a significant environmental impact due to their energy consumption and carbon footprint.
- The energy consumption of data centers is expected to continue to increase as more data is generated and stored.
- Data centers contribute to air pollution through emissions from power generation and cooling systems.
- Water resources can be impacted by data centers through their use in cooling systems and the disposal of wastewater.
- Land use can be affected by the construction and expansion of data centers, potentially leading to habitat loss and fragmentation.
The energy consumption of data centers
Data centers are notorious for their high energy consumption. They require a constant power supply to operate their servers, cooling systems, and other equipment. According to estimates, data centers consume about 1% of the world’s electricity.
To put this into perspective, the energy consumption of data centers is comparable to that of entire countries. In 2018, data centers in the United States alone consumed about 90 billion kilowatt-hours of electricity, which is equivalent to the energy used by 34 million average American homes in a year.
Several factors contribute to the energy consumption of data centers. First and foremost is the sheer number of servers required to handle the massive amounts of data. Additionally, the cooling systems used to maintain optimal temperatures in data centers also consume a significant amount of energy. Finally, inefficient infrastructure and outdated equipment can further contribute to energy waste in data centers.
The carbon footprint of data centers
The energy consumption of data centers directly translates into greenhouse gas emissions and contributes to their carbon footprint. The primary source of these emissions is the burning of fossil fuels for electricity generation.
Data centers are responsible for approximately 0.3% of global carbon dioxide emissions. To put this into perspective, this is roughly equivalent to the emissions of the entire aviation industry. If left unchecked, the carbon footprint of data centers is projected to increase significantly in the coming years.
Several factors contribute to the carbon footprint of data centers. As mentioned earlier, the energy consumption of data centers is a significant factor. The type of energy source used also plays a crucial role. Data centers that rely on fossil fuels for electricity generation have a higher carbon footprint compared to those powered by renewable energy sources.
The impact of data centers on air quality
| Metrics | Data Centers | Air Quality |
|---|---|---|
| CO2 Emissions | 2% of global emissions | Contributes to climate change |
| Energy Consumption | 1-3% of global energy consumption | Can lead to increased air pollution from power generation |
| Water Usage | Can consume up to 1500 gallons of water per minute | Can lead to water scarcity and impact air quality through reduced water availability for agriculture and other uses |
| Electronic Waste | Can contribute to electronic waste and toxic chemicals in landfills | Can lead to air pollution from incineration of electronic waste |
Data centers can have a significant impact on air quality due to the pollutants they emit. The primary source of these pollutants is the combustion of fossil fuels for electricity generation.
The most common pollutants emitted by data centers include carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur oxides (SOx), and particulate matter (PM). These pollutants can contribute to climate change, smog formation, and respiratory problems.
While data centers are not the largest contributors to air pollution, their impact should not be underestimated. In areas with a high concentration of data centers, such as Silicon Valley, the cumulative effect of emissions from multiple facilities can have a noticeable impact on air quality.
The impact of data centers on water resources
Data centers also have an impact on water resources due to their high water consumption. Water is used for cooling purposes in data centers, and the amount required can be substantial.
The water consumption of data centers varies depending on factors such as climate, cooling technology, and efficiency measures. On average, data centers consume about 4-6 liters of water per kilowatt-hour of electricity consumed.
While this may not seem like much, the cumulative effect of multiple data centers in an area can strain local water resources, especially in regions already facing water scarcity issues. Additionally, the discharge of heated water from cooling systems can also have a negative impact on aquatic ecosystems.
The impact of data centers on land use
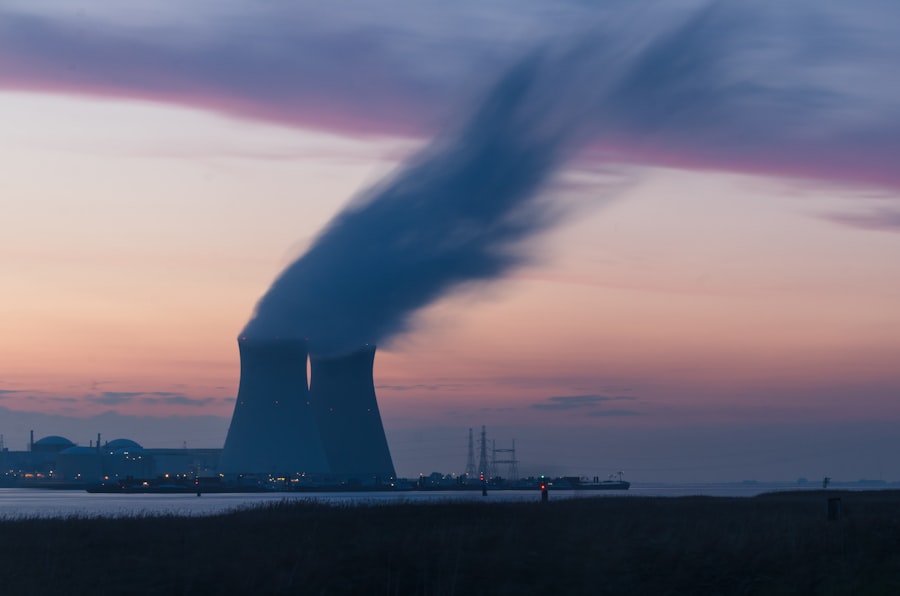


Data centers require a significant amount of land to accommodate their infrastructure. This can have an impact on land use, particularly in areas where land is already scarce or valuable.
The amount of land required for data centers depends on factors such as the size of the facility, the number of servers, and the supporting infrastructure. Large-scale data centers can occupy hundreds of acres of land.
The expansion of data centers can lead to deforestation, habitat destruction, and displacement of local communities. It is crucial to consider the environmental and social implications when siting new data centers.
The impact of data centers on biodiversity
Data centers can have a direct and indirect impact on biodiversity. The direct impact comes from the destruction of habitats during the construction and operation of data centers. The indirect impact comes from the emissions and pollution generated by data centers, which can contribute to climate change and disrupt ecosystems.
The construction of data centers often involves clearing land, which can result in the loss of biodiversity-rich habitats. Additionally, the operation of data centers can contribute to climate change, which is one of the biggest threats to biodiversity worldwide.
Furthermore, the emissions and pollutants generated by data centers can have a negative impact on local wildlife and ecosystems. For example, nitrogen oxides (NOx) emitted by data centers can contribute to acid rain, which can harm aquatic ecosystems.
The impact of data centers on e-waste
Data centers also contribute to the growing problem of electronic waste or e-waste. E-waste refers to discarded electronic devices such as servers, switches, and storage systems.
As technology advances and data centers upgrade their equipment, older devices become obsolete and need to be disposed of. Unfortunately, e-waste often ends up in landfills or is exported to developing countries with lax regulations for proper disposal.
E-waste contains hazardous materials such as lead, mercury, and cadmium, which can leach into the soil and water, posing a threat to human health and the environment. It is crucial for data centers to adopt responsible e-waste management practices to minimize their impact.
Sustainable practices for data centers
To address the environmental impact of data centers, it is essential to adopt sustainable practices. One of the most effective ways to reduce the environmental impact of data centers is to transition to renewable energy sources.
Renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power can provide a clean and sustainable source of electricity for data centers. Many companies are already investing in renewable energy projects or purchasing renewable energy credits to offset their carbon footprint.
In addition to renewable energy, data centers can also implement energy-efficient technologies and practices. This includes using energy-efficient servers and cooling systems, optimizing airflow management, and implementing virtualization and consolidation techniques to reduce the number of physical servers required.
Conclusion and future outlook for the environmental impact of data centers
In conclusion, data centers play a crucial role in modern society but also have a significant environmental impact. They consume vast amounts of energy, emit greenhouse gases, contribute to air pollution, strain water resources, occupy land, disrupt biodiversity, and generate e-waste.
Addressing the environmental impact of data centers is essential for a sustainable future. This includes transitioning to renewable energy sources, implementing energy-efficient technologies, adopting responsible e-waste management practices, and considering the environmental and social implications when siting new data centers.
The future outlook for sustainable data centers is promising. Many companies are recognizing the importance of sustainability and are taking steps to reduce their environmental footprint. The development of innovative technologies and practices will continue to drive progress in creating more sustainable data centers. By prioritizing sustainability, we can ensure that data centers continue to play a vital role in our digital world without compromising the health of our planet.
If you’re interested in learning more about the environmental impact of data centers, you might also want to check out this informative article on “Unlocking the Power of Data Center Rack Density: Best Practices and Strategies for Improved Performance and Cost Savings.” This article delves into the importance of optimizing rack density in data centers to maximize efficiency and reduce energy consumption. It provides valuable insights and strategies for improving performance while minimizing the environmental footprint of data centers. Read more
FAQs
What is a data center?
A data center is a facility used to house computer systems and associated components, such as telecommunications and storage systems.
What is the environmental impact of data centers?
Data centers have a significant environmental impact due to their high energy consumption, which contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. They also generate heat, which requires additional energy for cooling.
How much energy do data centers consume?
Data centers consume a significant amount of energy, accounting for approximately 1-2% of global electricity consumption. This is expected to increase as more data is generated and stored.
What are some ways to reduce the environmental impact of data centers?
There are several ways to reduce the environmental impact of data centers, including using renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency through better cooling and power management, and implementing virtualization and cloud computing technologies.
What are some companies doing to reduce the environmental impact of their data centers?
Many companies are taking steps to reduce the environmental impact of their data centers, including Google, which has committed to using 100% renewable energy for its data centers, and Microsoft, which has implemented a carbon fee to incentivize emissions reductions. Other companies are exploring innovative solutions such as underwater data centers and using waste heat to power nearby buildings.
Data center management refers to the process of overseeing and controlling the operations of a data center. A data center is a facility that houses computer systems and associated components, such as telecommunications and storage systems. It plays a crucial role in modern business operations, as it is responsible for storing, managing, and processing large amounts of data.
In today’s digital age, data centers have become the backbone of many organizations. They are essential for storing and accessing critical business information, supporting applications and services, and ensuring the smooth operation of IT infrastructure. Without effective data center management, businesses may face significant challenges in terms of data security, availability, and performance.
Data center managers face a range of challenges in their role. They must ensure the efficient operation of the data center, optimize its performance, and minimize downtime. They also need to manage resources effectively, plan for future capacity needs, implement energy-efficient solutions, and address security risks. These challenges require a deep understanding of data center operations and the ability to implement best practices for optimal performance.
Key Takeaways
- Data center management is crucial for businesses to ensure efficient and effective operations.
- Optimizing data center performance can lead to cost savings and improved productivity.
- Best practices for data center performance optimization include regular maintenance, monitoring, and capacity planning.
- Key components of efficient data center management include power and cooling systems, network infrastructure, and storage solutions.
- Strategies for reducing data center downtime include implementing redundancy and disaster recovery plans.
Understanding the Importance of Data Center Optimization
Data center optimization refers to the process of improving the performance and efficiency of a data center. It involves analyzing and fine-tuning various aspects of the data center, such as infrastructure, hardware, software, and processes. By optimizing data center performance, organizations can achieve several benefits.
One of the key benefits of data center optimization is improved operational efficiency. By identifying and addressing bottlenecks or inefficiencies in the data center, organizations can streamline their processes and reduce costs. This can lead to increased productivity and better resource utilization.
Data center optimization also helps organizations enhance their overall business operations. By improving the performance and availability of critical applications and services, organizations can deliver better customer experiences and gain a competitive edge in the market. It also enables organizations to scale their operations more effectively and support future growth.
Best Practices for Data Center Performance Optimization
To optimize data center performance, organizations should follow best practices that focus on monitoring and analyzing data center performance, improving efficiency, and reducing downtime.
Monitoring and analyzing data center performance is crucial for identifying bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and potential issues. By collecting and analyzing data on key performance indicators (KPIs), such as power usage, temperature, and network latency, organizations can gain insights into the health and performance of their data center. This allows them to proactively address any issues before they impact business operations.
Improving efficiency is another important aspect of data center performance optimization. This can be achieved through various strategies, such as virtualization, consolidation, and automation. Virtualization allows organizations to run multiple virtual machines on a single physical server, reducing hardware costs and improving resource utilization. Consolidation involves combining multiple servers or storage systems into a single, more efficient unit. Automation helps streamline processes and reduce manual intervention, leading to increased efficiency and reduced human error.
Reducing downtime is a critical goal for data center managers. Downtime can result in significant financial losses, damage to reputation, and loss of customer trust. To minimize downtime, organizations should focus on proactive maintenance and monitoring. This includes regular equipment inspections, preventive maintenance activities, and continuous monitoring of critical systems. By identifying potential issues early on and taking proactive measures to address them, organizations can minimize the risk of unplanned downtime.
Key Components of Efficient Data Center Management
Efficient data center management requires attention to several key components, including infrastructure, hardware, and software management.
Infrastructure management involves overseeing the physical components of the data center, such as power distribution units (PDUs), cooling systems, and cabling infrastructure. It is important to ensure that the infrastructure is designed and maintained to support the needs of the data center. This includes proper power distribution, cooling capacity planning, and cable management to minimize the risk of equipment failure or downtime.
Hardware management involves the proper maintenance and monitoring of servers, storage systems, and networking equipment. This includes regular hardware inspections, firmware updates, and performance monitoring. It is important to ensure that hardware components are functioning optimally and are capable of meeting the demands of the data center.
Software management involves the installation, configuration, and maintenance of software applications and operating systems in the data center. This includes regular software updates, patch management, and security monitoring. It is important to ensure that software applications are up-to-date and secure to minimize the risk of vulnerabilities or system failures.
Effective management of these key components is crucial for ensuring the smooth operation of the data center and maximizing its performance.
Strategies for Reducing Data Center Downtime
Data center downtime can have severe consequences for organizations, including financial losses, damage to reputation, and loss of customer trust. To reduce downtime and improve data center availability, organizations should focus on proactive maintenance and monitoring.
One of the main causes of data center downtime is equipment failure. By implementing a proactive maintenance program, organizations can identify potential issues before they cause a system failure. This includes regular equipment inspections, preventive maintenance activities, and replacement of aging or faulty components. By addressing potential issues early on, organizations can minimize the risk of unplanned downtime.
Continuous monitoring is another important strategy for reducing downtime. By monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs), such as temperature, power usage, and network latency, organizations can identify potential issues or anomalies that may lead to downtime. This allows them to take proactive measures to address these issues before they impact business operations.
Redundancy is another key strategy for reducing downtime. By implementing redundant systems or components, organizations can ensure that there is a backup in case of a failure. This includes redundant power supplies, network connections, and storage systems. By having redundant systems in place, organizations can minimize the impact of a failure and maintain business continuity.
Effective Data Center Capacity Planning


Effective capacity planning is crucial for data center management. It involves forecasting future capacity needs and ensuring that the data center has the necessary resources to meet those needs. By effectively planning for capacity, organizations can avoid overprovisioning or underprovisioning of resources, which can lead to inefficiencies or downtime.
To effectively plan for capacity, organizations should consider several factors, such as current and projected data storage requirements, computing power needs, and network bandwidth requirements. This involves analyzing historical data, understanding business growth plans, and considering technological advancements that may impact capacity needs.
Scalability and flexibility are important considerations in capacity planning. Organizations should ensure that their data center infrastructure is scalable and can easily accommodate future growth. This includes having the ability to add or remove servers, storage systems, or networking equipment as needed. Flexibility is also important to adapt to changing business needs or technological advancements.
By effectively planning for capacity, organizations can ensure that their data center has the necessary resources to support current and future business operations. This helps minimize the risk of downtime, improve performance, and support business growth.
Implementing Energy-Efficient Solutions in Data Centers
Energy efficiency is a critical aspect of data center management. Data centers consume a significant amount of energy, and reducing energy consumption not only helps organizations reduce costs but also contributes to environmental sustainability.
To implement energy-efficient solutions in data centers, organizations should consider several strategies. One strategy is virtualization, which allows organizations to run multiple virtual machines on a single physical server. This reduces the number of physical servers required, leading to lower energy consumption and reduced cooling needs.
Another strategy is consolidation, which involves combining multiple servers or storage systems into a single, more efficient unit. This reduces the overall energy consumption and improves resource utilization. Organizations can also consider using energy-efficient hardware components, such as servers with low-power processors or solid-state drives (SSDs) that consume less energy than traditional hard disk drives (HDDs).
Efficient cooling is another important aspect of energy efficiency in data centers. By implementing efficient cooling systems, such as hot aisle/cold aisle containment or liquid cooling, organizations can reduce the energy required for cooling and improve overall energy efficiency.
Reducing energy consumption in data centers not only helps organizations reduce costs but also contributes to environmental sustainability. By implementing energy-efficient solutions, organizations can reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to a greener future.
Data Center Security and Risk Management
Data center security and risk management are critical aspects of data center management. Data centers house valuable and sensitive information, and any security breach or data loss can have severe consequences for organizations.
To manage data center security risks, organizations should implement several strategies. One strategy is to implement physical security measures, such as access controls, surveillance cameras, and biometric authentication systems. This helps prevent unauthorized access to the data center and protects against physical threats.
Another strategy is to implement network security measures, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and encryption. This helps protect against cyber threats, such as hacking or malware attacks. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are also important to identify potential vulnerabilities and address them before they are exploited.
Disaster recovery and business continuity planning are also crucial for data center management. Organizations should have a comprehensive plan in place to recover from a disaster or system failure and ensure the continuity of critical business operations. This includes regular backups of data, testing of disaster recovery plans, and training of staff on emergency procedures.
By effectively managing data center security risks and implementing robust risk management strategies, organizations can protect their valuable data and ensure the continuity of critical business operations.
Managing Data Center Costs and Budgets
Managing data center costs and budgets is an important aspect of data center management. Data centers can be expensive to operate, and organizations need to ensure that they are making efficient use of their resources and optimizing their investments.
To reduce data center costs, organizations should consider several strategies. One strategy is to optimize resource utilization. This includes consolidating servers or storage systems, implementing virtualization, and automating processes to improve efficiency and reduce the number of physical resources required.
Another strategy is to implement energy-efficient solutions, as discussed earlier. By reducing energy consumption, organizations can significantly reduce their energy costs. This includes implementing efficient cooling systems, using energy-efficient hardware components, and optimizing power distribution.
Regular maintenance and monitoring are also important for managing costs. By proactively addressing potential issues or inefficiencies, organizations can minimize the risk of downtime and reduce the costs associated with equipment failure or system outages.
Optimizing data center investments is another important aspect of managing costs. Organizations should regularly review their hardware and software investments to ensure that they are aligned with business needs and technological advancements. This includes retiring outdated or underutilized equipment and investing in new technologies that can improve performance and efficiency.
By effectively managing costs and budgets, organizations can optimize their data center investments and ensure that they are making efficient use of their resources.
Future Trends in Data Center Management
Data center management is a rapidly evolving field, and it is important for organizations to stay up-to-date with the latest technologies and practices. Several emerging trends are shaping the future of data center management.
One trend is the adoption of cloud computing. Cloud computing allows organizations to access computing resources on-demand, without the need for physical infrastructure. This provides flexibility, scalability, and cost savings. Organizations are increasingly moving their applications and services to the cloud, which has implications for data center management. Data center managers need to understand how to effectively manage hybrid environments that include both on-premises data centers and cloud infrastructure.
Another trend is the increasing use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in data center management. AI and ML technologies can analyze large amounts of data and identify patterns or anomalies that may impact data center performance. This allows organizations to proactively address potential issues and optimize their data center operations. AI and ML can also be used for predictive maintenance, where algorithms can predict equipment failures before they occur, reducing downtime and improving reliability.
Green data centers are also becoming more prevalent. Green data centers focus on energy efficiency and environmental sustainability. They use renewable energy sources, implement efficient cooling systems, and optimize resource utilization to reduce energy consumption and carbon footprint. As organizations become more conscious of their environmental impact, green data centers will become increasingly important.
In conclusion, data center management is a critical aspect of modern business operations. Effective data center management involves optimizing performance, reducing downtime, managing resources effectively, ensuring security and risk management, managing costs and budgets, and staying up-to-date with the latest technologies and practices. By implementing best practices and strategies for data center management, organizations can ensure the smooth operation of their data centers, improve business operations, and gain a competitive edge in the market.
If you’re interested in learning more about data center management and optimizing operations and performance, you may also find the article “The Art of Data Center Relocation: Maximizing Efficiency and Minimizing Downtime” to be valuable. This informative piece, available at datacenterinfo.com, explores the intricacies of relocating a data center while ensuring maximum efficiency and minimal downtime. It provides insights and strategies for successfully managing the complex process of moving a data center, making it a must-read for anyone involved in data center management.
FAQs
What is data center management?
Data center management refers to the process of overseeing and maintaining the operations of a data center, which includes managing hardware, software, and networking components.
Why is data center management important?
Data center management is important because it ensures that the data center is operating efficiently and effectively, which can help to reduce downtime, improve performance, and increase the lifespan of equipment.
What are some strategies for optimizing data center operations?
Some strategies for optimizing data center operations include implementing virtualization, using energy-efficient hardware, monitoring and managing power usage, and implementing automation and orchestration tools.
What is virtualization?
Virtualization is the process of creating a virtual version of something, such as a server, operating system, storage device, or network resource. This allows multiple virtual instances to run on a single physical machine, which can help to reduce costs and improve efficiency.
What is energy-efficient hardware?
Energy-efficient hardware refers to computer hardware that is designed to use less energy than traditional hardware. This can include servers, storage devices, and networking equipment that are designed to consume less power and generate less heat.
What is power usage monitoring and management?
Power usage monitoring and management involves tracking the amount of power being used by data center equipment and implementing strategies to reduce power consumption. This can include using energy-efficient hardware, implementing power management policies, and using tools to monitor and manage power usage.
What are automation and orchestration tools?
Automation and orchestration tools are software tools that automate and streamline data center operations. This can include automating routine tasks, such as server provisioning and software updates, and using orchestration tools to manage complex workflows and processes.
Disaster recovery planning is the process of creating a strategy and set of procedures to ensure the continuity of business operations in the event of a disaster. This can include natural disasters such as hurricanes or earthquakes, as well as human-caused disasters like cyber attacks or power outages. The goal of disaster recovery planning is to minimize the impact of a disaster on a business and enable it to recover quickly and efficiently.
Disaster recovery planning is crucial for businesses of all sizes and industries. In today’s digital age, where data is the lifeblood of many organizations, the loss or unavailability of critical systems and data can have severe consequences. Without a well-thought-out disaster recovery plan, businesses risk losing valuable data, experiencing prolonged downtime, and suffering financial losses. Therefore, it is essential for businesses to prioritize disaster recovery planning to protect their operations and ensure their long-term success.
In this blog post, we will explore the importance of business continuity in data centers, the types of disasters that can affect data centers, how to assess risks and identify critical systems, steps in developing a disaster recovery plan, testing and evaluating the plan, implementing the plan during a disaster, communication and collaboration in disaster recovery, training and education for disaster preparedness, and continuous improvement through reviewing and updating the plan.
Key Takeaways
- Disaster recovery planning is essential for businesses to ensure continuity of operations in the event of a disaster.
- Data centers are critical to business continuity and require special attention in disaster recovery planning.
- Disasters that can affect data centers include natural disasters, cyber attacks, and human error.
- Risks must be assessed and critical systems identified to develop an effective disaster recovery plan.
- Testing, evaluating, and continuous improvement are necessary to ensure the plan is effective and up-to-date.
The Importance of Business Continuity in Data Centers
Business continuity refers to the ability of an organization to continue its operations without interruption or minimal disruption in the face of a disaster. In the context of data centers, business continuity is crucial because these facilities house critical systems and data that are essential for the functioning of businesses. A disruption in a data center can have severe consequences for an organization, including financial losses, damage to reputation, and loss of customer trust.
Data center downtime can have a significant impact on businesses. According to a study by Ponemon Institute, the average cost of data center downtime is $9,000 per minute. This includes direct costs such as lost revenue and increased expenses, as well as indirect costs such as damage to reputation and customer churn. In addition, downtime can result in data loss, which can be catastrophic for businesses that rely on their data for decision-making and operations.
To ensure business continuity in data centers, it is essential to have a robust disaster recovery plan in place. This plan should outline the steps to be taken in the event of a disaster, including backup and recovery procedures, alternative power sources, and communication protocols. By having a well-prepared disaster recovery plan, businesses can minimize the impact of a disaster on their operations and recover quickly, thus ensuring their long-term success.
Types of Disasters That Can Affect Data Centers
Data centers are vulnerable to various types of disasters that can disrupt their operations. These disasters can be classified into three main categories: natural disasters, human-caused disasters, and other potential disasters.
Natural disasters such as hurricanes, earthquakes, floods, and wildfires can cause significant damage to data centers. These events can result in power outages, physical damage to infrastructure, and loss of connectivity. For example, during Hurricane Sandy in 2012, many data centers in the affected areas experienced prolonged downtime due to flooding and power outages.
Human-caused disasters include cyber attacks, power outages, and equipment failures. Cyber attacks are a growing threat to data centers, with hackers targeting sensitive data and disrupting operations. Power outages can occur due to equipment failures or grid failures, resulting in the loss of power to data centers. Equipment failures can also lead to downtime if critical systems fail or become unavailable.
Other potential disasters that can affect data centers include pandemics and terrorist attacks. Pandemics like the COVID-19 pandemic can disrupt operations by forcing employees to work remotely or causing supply chain disruptions. Terrorist attacks can result in physical damage to data centers or infrastructure, as well as loss of connectivity.
To ensure the continuity of operations in the face of these disasters, it is crucial to have a comprehensive disaster recovery plan that addresses each type of disaster and outlines the necessary steps to be taken.
Assessing Risks and Identifying Critical Systems
Before developing a disaster recovery plan, it is essential to assess the risks that a business may face and identify the critical systems and data that need to be protected. Risk assessment involves identifying potential threats, evaluating their likelihood and impact, and determining the level of risk they pose to the organization.
The risk assessment process typically involves conducting a thorough analysis of the business’s operations, infrastructure, and vulnerabilities. This can include reviewing past incidents, conducting site visits, and engaging with stakeholders. The goal is to identify potential risks and prioritize them based on their likelihood and impact on the organization.
Once the risks have been assessed, it is important to identify the critical systems and data that need to be protected. Critical systems are those that are essential for the functioning of the business and cannot afford prolonged downtime. This can include customer databases, financial systems, communication systems, and other mission-critical applications.
By assessing risks and identifying critical systems, businesses can prioritize their resources and efforts in developing a disaster recovery plan that focuses on protecting the most important aspects of their operations.
Developing a Disaster Recovery Plan
Developing a disaster recovery plan involves several steps to ensure that all aspects of the business’s operations are covered in the event of a disaster. These steps include:
1. Establishing goals and objectives: Define the goals and objectives of the disaster recovery plan, such as minimizing downtime, protecting critical systems and data, and ensuring the safety of employees.
2. Conducting a business impact analysis: Identify the potential impacts of a disaster on the business, including financial losses, damage to reputation, and loss of customer trust. This analysis will help prioritize the recovery efforts and allocate resources effectively.
3. Developing recovery strategies: Determine the strategies and procedures to be followed in the event of a disaster. This can include backup and recovery procedures, alternative power sources, communication protocols, and relocation plans.
4. Documenting the plan: Document all aspects of the disaster recovery plan, including the goals and objectives, recovery strategies, contact information, and procedures. This documentation should be easily accessible to all relevant stakeholders.
5. Training and education: Train employees on their roles and responsibilities during a disaster and provide them with the necessary knowledge and skills to execute the plan effectively. This can include conducting drills, tabletop exercises, and online courses.
6. Testing and evaluating the plan: Regularly test the disaster recovery plan to ensure its effectiveness and identify any gaps or weaknesses. This can include tabletop exercises, full-scale simulations, and post-exercise evaluations.
By following these steps, businesses can develop a comprehensive disaster recovery plan that addresses all potential risks and ensures the continuity of their operations in the face of a disaster.
Testing and Evaluating the Plan


Testing and evaluating the disaster recovery plan is a critical step in ensuring its effectiveness and identifying any gaps or weaknesses. Testing allows businesses to simulate various disaster scenarios and assess their readiness to respond and recover from these events.
There are several types of testing that can be conducted, including tabletop exercises, full-scale simulations, and post-exercise evaluations. Tabletop exercises involve walking through the disaster recovery plan with key stakeholders to identify any issues or areas for improvement. Full-scale simulations involve executing the plan in a controlled environment to test its effectiveness in a real-world scenario. Post-exercise evaluations involve reviewing the results of the testing and identifying any lessons learned or areas for improvement.
Testing should be conducted regularly to ensure that the disaster recovery plan remains up-to-date and effective. As technology evolves and new threats emerge, it is important to adapt the plan accordingly and test its effectiveness in addressing these new challenges.
Implementing the Plan: Response and Recovery
During a disaster, it is crucial to have well-defined response and recovery procedures in place to ensure the continuity of operations and minimize the impact on the business. Response procedures involve the immediate actions to be taken when a disaster occurs, such as activating the emergency response team, notifying employees and stakeholders, and implementing emergency communication protocols.
Recovery procedures involve the steps to be taken after the initial response to restore operations and recover from the disaster. This can include restoring critical systems and data from backups, repairing or replacing damaged infrastructure, and implementing alternative power sources. It is important to document all actions taken during the recovery process and track progress to ensure that all necessary steps are completed.
Documentation is a crucial aspect of implementing the plan as it provides a record of the actions taken, decisions made, and progress achieved during the response and recovery process. This documentation can be used for future reference, training purposes, and continuous improvement.
Communication and Collaboration in Disaster Recovery
Effective communication is essential during a disaster to ensure that all relevant stakeholders are informed and updated on the situation. This includes internal communication within the organization, as well as external communication with customers, vendors, and other external stakeholders.
Internal communication involves notifying employees about the disaster, providing them with instructions on what to do, and keeping them updated on the progress of the recovery efforts. This can include using various communication channels such as email, phone calls, text messages, and collaboration tools.
Collaboration between IT and other departments is also crucial during a disaster to ensure that all aspects of the business’s operations are covered. IT should work closely with other departments such as finance, operations, and customer service to coordinate the response and recovery efforts. This can include sharing information, coordinating resources, and aligning priorities.
External communication involves keeping customers, vendors, and other external stakeholders informed about the situation and the steps being taken to recover from the disaster. This can include sending regular updates, setting up a dedicated communication channel, and providing support and assistance as needed.
By prioritizing communication and collaboration during a disaster, businesses can ensure that all relevant stakeholders are informed and involved in the response and recovery efforts, thus minimizing the impact of the disaster on their operations.
Training and Education for Disaster Preparedness
Training and education are essential for disaster preparedness as they provide employees with the knowledge and skills to respond effectively to a disaster. This includes understanding their roles and responsibilities, knowing how to execute the disaster recovery plan, and being aware of the potential risks and threats.
There are various types of training that can be conducted to prepare employees for a disaster. This can include drills, tabletop exercises, online courses, and workshops. Drills involve simulating various disaster scenarios to test employees’ readiness to respond and recover. Tabletop exercises involve walking through the disaster recovery plan with key stakeholders to identify any issues or areas for improvement. Online courses provide employees with the necessary knowledge and skills to execute the plan effectively.
In addition to training, it is important to involve employees in the disaster recovery planning process. This can include soliciting their input, incorporating their feedback, and empowering them to take ownership of their roles and responsibilities. By involving employees in the planning process, businesses can ensure that all aspects of their operations are covered and that everyone is prepared to respond effectively in the event of a disaster.
Continuous Improvement: Reviewing and Updating the Plan
Disaster recovery planning is an ongoing process that requires regular review and updates to ensure its effectiveness. As technology evolves, new threats emerge, and business operations change, it is important to adapt the plan accordingly.
Regular reviews of the plan should be conducted to identify any gaps or weaknesses and make necessary updates. This can include reviewing past incidents, conducting risk assessments, and engaging with stakeholders. Lessons learned from previous disasters should be incorporated into the plan to improve its effectiveness and ensure that the same mistakes are not repeated.
The frequency of plan updates will depend on the specific needs and requirements of the business. However, it is generally recommended to review and update the plan at least annually or whenever there are significant changes in the business’s operations or infrastructure.
By continuously reviewing and updating the disaster recovery plan, businesses can ensure that they are prepared to respond effectively to a disaster and minimize its impact on their operations.
In conclusion, disaster recovery planning is crucial for businesses to ensure the continuity of their operations in the face of a disaster. By developing a comprehensive disaster recovery plan, businesses can minimize the impact of a disaster on their operations, protect critical systems and data, and recover quickly and efficiently. This requires assessing risks, identifying critical systems, developing recovery strategies, testing and evaluating the plan, implementing response and recovery procedures, prioritizing communication and collaboration, providing training and education, and continuously reviewing and updating the plan.
The importance of disaster recovery planning cannot be overstated. In today’s digital age, where data is the lifeblood of many organizations, the loss or unavailability of critical systems and data can have severe consequences. Without a well-thought-out disaster recovery plan, businesses risk losing valuable data, experiencing prolonged downtime, and suffering financial losses. Therefore, it is essential for businesses to prioritize disaster recovery planning to protect their operations and ensure their long-term success.
In light of the importance of disaster recovery planning, businesses should take immediate action to assess their risks, identify critical systems, develop a comprehensive plan, and regularly review and update it. By doing so, they can ensure that they are prepared to respond effectively to a disaster and minimize its impact on their operations.
If you’re interested in disaster recovery planning and ensuring business continuity in data centers, you may also find this article on understanding data center tiers helpful. It explains what data center tiers are and why they matter in terms of reliability, redundancy, and uptime. Understanding the different tiers can help you make informed decisions when it comes to disaster recovery planning and choosing the right data center for your business needs. Check out the article here for more information.
FAQs
What is disaster recovery planning?
Disaster recovery planning is the process of creating a plan to recover from a disaster or disruptive event that affects a business’s critical operations and infrastructure.
Why is disaster recovery planning important?
Disaster recovery planning is important because it ensures that a business can continue to operate in the event of a disaster or disruptive event. It helps to minimize downtime, reduce data loss, and protect the business’s reputation.
What are the key components of a disaster recovery plan?
The key components of a disaster recovery plan include identifying potential risks and threats, establishing recovery objectives, creating a communication plan, developing a backup and recovery strategy, and testing and updating the plan regularly.
What are the different types of disasters that can affect a data center?
The different types of disasters that can affect a data center include natural disasters such as earthquakes, hurricanes, and floods, as well as man-made disasters such as cyber attacks, power outages, and equipment failures.
What are the best practices for disaster recovery planning?
The best practices for disaster recovery planning include conducting a risk assessment, establishing recovery time objectives, creating a communication plan, implementing a backup and recovery strategy, testing and updating the plan regularly, and training employees on the plan.
Data center services refer to the management and operation of a facility that houses computer systems and associated components, such as telecommunications and storage systems. These services are essential for modern businesses as they provide a secure and reliable environment for storing, processing, and managing data. Data center services include a range of activities, such as server hosting, network management, data backup and recovery, and security monitoring.
In today’s digital age, businesses rely heavily on technology to operate efficiently and effectively. The amount of data generated by businesses is growing exponentially, and it is crucial to have a robust infrastructure in place to handle this data. Data center services play a vital role in ensuring that businesses can store, process, and access their data securely and reliably. Without these services, businesses would face significant challenges in managing their data and meeting the demands of their customers.
Key Takeaways
- Data center services can be outsourced or managed in-house.
- Outsourcing data center services can provide cost savings and access to technical expertise.
- In-house data center management offers greater control and customization.
- Cost comparison should be considered when deciding between outsourcing and in-house management.
- Security, scalability, and technical support are important factors to consider when choosing between outsourcing and in-house management.
Understanding Outsourcing and In-House Management
Outsourcing refers to the practice of hiring an external service provider to handle specific business functions or processes. In the context of data center services, outsourcing involves contracting with a third-party provider to manage and operate the data center facility. In contrast, in-house management refers to the practice of managing and operating the data center facility internally within the organization.
The main difference between outsourcing and in-house management lies in who is responsible for the day-to-day operations of the data center facility. With outsourcing, the service provider takes on the responsibility of managing and operating the facility, while with in-house management, the organization retains full control over the operations.
Benefits of Outsourcing Data Center Services
1. Cost savings: One of the primary benefits of outsourcing data center services is cost savings. By outsourcing, businesses can avoid the upfront costs associated with building and maintaining their own data center facility. They also benefit from economies of scale as service providers can spread their costs across multiple clients, resulting in lower overall costs for each client.
2. Access to specialized expertise: Outsourcing data center services allows businesses to tap into the specialized expertise of service providers. These providers have extensive knowledge and experience in managing data center facilities, ensuring that businesses can benefit from best practices and the latest technologies. This expertise is particularly valuable for businesses that do not have the resources or expertise to manage a data center facility effectively.
3. Improved scalability and flexibility: Outsourcing data center services provides businesses with the ability to scale their operations quickly and easily. Service providers have the infrastructure and resources in place to accommodate changing business needs, such as increased storage capacity or additional computing power. This scalability and flexibility allow businesses to adapt to market demands and seize new opportunities without the need for significant capital investments.
4. Reduced risk and increased security: Data security is a top concern for businesses, and outsourcing data center services can help mitigate this risk. Service providers have robust security measures in place, including physical security, fire suppression systems, and advanced cybersecurity protocols. By outsourcing, businesses can benefit from these security measures without having to invest heavily in their own security infrastructure.
Benefits of In-House Data Center Management
1. Greater control and customization: In-house data center management provides businesses with greater control over their operations. They have full control over the design, configuration, and management of the data center facility, allowing them to customize it to meet their specific needs and requirements. This level of control is particularly important for businesses with unique or complex IT infrastructure requirements.
2. Improved security and compliance: In-house data center management allows businesses to have complete control over their security measures and compliance protocols. They can implement stringent security measures tailored to their specific needs and industry regulations. This level of control provides businesses with peace of mind knowing that they have full visibility and control over their data security.
3. Better alignment with business goals and objectives: In-house data center management enables businesses to align their data center operations with their overall business goals and objectives. They can prioritize resources and investments based on their specific needs and strategic priorities. This alignment ensures that the data center facility is fully optimized to support the organization’s growth and success.
Cost Comparison: Outsourcing vs. In-House Management
When comparing the costs of outsourcing data center services versus in-house management, several factors need to be considered.
1. Infrastructure costs: Building and maintaining a data center facility can be a significant capital investment for businesses. Outsourcing eliminates the need for these upfront costs, as service providers already have the infrastructure in place. However, businesses need to consider the long-term costs of outsourcing, such as monthly service fees and potential price increases over time.
2. Operational costs: In-house management requires businesses to allocate resources for hiring and training staff, purchasing equipment, and maintaining the facility. These operational costs can add up over time. On the other hand, outsourcing transfers these operational costs to the service provider, who can leverage economies of scale to provide cost-effective services.
3. Scalability and flexibility: Outsourcing data center services provides businesses with greater scalability and flexibility without the need for significant capital investments. In-house management may require businesses to invest in additional infrastructure to accommodate growth or changes in demand.
Real-world examples can help illustrate the cost comparison between outsourcing and in-house management. For example, a small startup with limited resources may find it more cost-effective to outsource data center services, as they can benefit from the expertise and infrastructure of a service provider without incurring significant upfront costs. On the other hand, a large enterprise with complex IT infrastructure requirements may find it more cost-effective to invest in building and managing an in-house data center facility to have full control over their operations.
Security Considerations in Data Center Services


Security is a critical consideration when it comes to data center services. Businesses must ensure that their data is protected from unauthorized access, data breaches, and other security threats.
Importance of security in data center services: Data centers house vast amounts of sensitive and valuable data, making them attractive targets for cybercriminals. A security breach can have severe consequences for businesses, including financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liabilities. Therefore, it is crucial to have robust security measures in place to protect data center facilities and the data they store.
Best practices for securing data center services: To enhance the security of data center services, businesses should implement a range of best practices. These include:
1. Physical security: Data center facilities should have strict access controls, including biometric authentication, video surveillance, and 24/7 security personnel. Only authorized personnel should be allowed access to the facility.
2. Network security: Data center networks should be protected by firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption protocols. Regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing should be conducted to identify and address any potential weaknesses.
3. Data encryption: All sensitive data stored in the data center should be encrypted to protect it from unauthorized access. Encryption should be applied both at rest and in transit.
4. Employee training: Employees who have access to the data center facility should receive regular training on security best practices and protocols. This training should cover topics such as password hygiene, social engineering awareness, and incident response procedures.
Risks and challenges associated with data center security: Despite implementing robust security measures, there are still risks and challenges associated with data center security. These include:
1. Insider threats: Employees with access to the data center facility can pose a significant risk if they misuse their privileges or intentionally compromise the security of the facility.
2. Advanced persistent threats: Cybercriminals are constantly evolving their tactics to bypass security measures. Advanced persistent threats (APTs) can target data center facilities and remain undetected for extended periods, making them difficult to mitigate.
3. Compliance requirements: Data center facilities must comply with various industry regulations and standards, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). Ensuring compliance can be challenging and requires ongoing monitoring and updates to security protocols.
Scalability and Flexibility in Data Center Services
Scalability and flexibility are crucial considerations in data center services, as businesses need to be able to adapt to changing demands and requirements.
Importance of scalability and flexibility in data center services: Businesses operate in dynamic environments where their data storage and processing needs can change rapidly. Scalability and flexibility in data center services allow businesses to scale their operations up or down quickly and efficiently, without the need for significant capital investments or disruptions to their operations.
Best practices for achieving scalability and flexibility: To achieve scalability and flexibility in data center services, businesses should consider the following best practices:
1. Virtualization: Virtualization allows businesses to separate their applications from the underlying hardware, making it easier to scale resources up or down as needed. By virtualizing their infrastructure, businesses can allocate resources dynamically based on demand.
2. Cloud computing: Leveraging cloud computing services can provide businesses with instant scalability and flexibility. Cloud service providers offer on-demand resources that can be easily scaled up or down based on business needs. This eliminates the need for businesses to invest in additional hardware or infrastructure.
3. Modular design: Designing data center facilities with a modular approach allows for easier scalability and flexibility. Modular components can be added or removed as needed, allowing businesses to scale their operations without disrupting existing infrastructure.
Risks and challenges associated with scalability and flexibility: While scalability and flexibility offer significant benefits, there are also risks and challenges associated with these capabilities. These include:
1. Cost management: Scaling resources up or down can impact costs, especially if not managed effectively. Businesses need to carefully monitor their resource usage and optimize their infrastructure to ensure cost efficiency.
2. Performance and latency: Scaling resources can impact performance and introduce latency if not properly managed. Businesses need to ensure that their infrastructure can handle increased demand without compromising performance.
3. Integration challenges: Scaling resources across different platforms or providers can introduce integration challenges. Businesses need to ensure that their systems can seamlessly integrate and communicate with each other to avoid disruptions or data inconsistencies.
Technical Expertise and Support in Data Center Services
Technical expertise and support are essential in data center services to ensure the smooth operation and maintenance of the facility.
Importance of technical expertise and support in data center services: Data center facilities require specialized knowledge and skills to operate effectively. Technical experts have the expertise to design, implement, and maintain the infrastructure, ensuring that it meets the needs of the business and operates at optimal performance.
Best practices for selecting and working with technical experts: To select and work effectively with technical experts in data center services, businesses should consider the following best practices:
1. Define requirements: Clearly define the technical requirements and objectives of the data center facility. This will help identify the specific expertise needed and ensure that technical experts have a clear understanding of the business’s needs.
2. Evaluate experience and qualifications: When selecting technical experts, evaluate their experience, qualifications, and track record in managing data center facilities. Look for certifications, industry recognition, and references from previous clients.
3. Establish clear communication channels: Establish clear communication channels with technical experts to ensure effective collaboration. Regular meetings, progress updates, and performance reviews can help maintain transparency and accountability.
Risks and challenges associated with technical expertise and support: While technical expertise is crucial in data center services, there are risks and challenges associated with relying on external experts. These include:
1. Dependency on external resources: Businesses may become overly reliant on external technical experts, making it challenging to transition to in-house management or switch service providers if needed.
2. Knowledge transfer and documentation: Technical experts may have specialized knowledge that is not well-documented or transferred to the business. This can create challenges when transitioning to a new service provider or when internal staff need to take over the management of the data center facility.
3. Vendor lock-in: Businesses may become locked into long-term contracts with service providers, limiting their flexibility and ability to switch providers if needed. It is essential to carefully review contracts and negotiate terms that allow for flexibility and scalability.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Outsourcing and In-House Management
When choosing between outsourcing data center services and in-house management, businesses need to consider several key factors:
1. Cost: Consider the upfront costs, operational costs, and long-term costs associated with both options. Evaluate the potential cost savings of outsourcing versus the benefits of having full control over operations with in-house management.
2. Expertise: Assess the technical expertise and support required for managing a data center facility. Determine whether the business has the necessary resources and expertise in-house or if it would benefit from outsourcing to a specialized service provider.
3. Scalability and flexibility: Evaluate the scalability and flexibility requirements of the business. Consider whether outsourcing would provide the necessary scalability and flexibility without significant capital investments or disruptions to operations.
4. Security: Assess the security measures and protocols required for protecting data center facilities. Consider whether outsourcing would provide the necessary security measures or if in-house management would allow for greater control over security.
5. Business goals and objectives: Align the decision with the overall goals and objectives of the business. Consider whether outsourcing or in-house management would better support the growth and success of the organization.
Real-world examples can provide insights into successful and unsuccessful outsourcing and in-house management decisions. For example, a large financial institution may choose to outsource data center services to a specialized service provider to benefit from their expertise, scalability, and security measures. On the other hand, a technology company with unique infrastructure requirements may opt for in-house management to have full control over their operations and customization.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business
Choosing between outsourcing data center services and in-house management is a critical decision that businesses must make based on their specific needs, requirements, and resources. Both options offer distinct benefits and challenges, and businesses need to carefully evaluate the factors discussed in this article to make an informed decision.
Outsourcing data center services can provide cost savings, access to specialized expertise, improved scalability and flexibility, and reduced risk. On the other hand, in-house management offers greater control and customization, improved security and compliance, and better alignment with business goals.
Ultimately, businesses need to assess their unique circumstances and prioritize their needs to determine whether outsourcing or in-house management is the right choice for their data center services. By considering the factors discussed in this article and learning from real-world examples, businesses can make an informed decision that aligns with their goals and objectives.
If you’re considering the best approach for managing your data center services, it’s important to weigh the pros and cons of outsourcing versus in-house management. In a recent article by Data Center Info, they explore this topic in depth and provide valuable insights for decision-makers. To further enhance your understanding, check out their related article on how Flexential Norcross can help you achieve peak performance and security through the power of the cloud. This article delves into the role of data centers in cloud computing and web hosting services, offering a comprehensive perspective on the benefits of leveraging external expertise. Read more here.
FAQs
What are data center services?
Data center services refer to the management and maintenance of a company’s data center infrastructure, including servers, storage, networking, and security.
What is outsourcing?
Outsourcing is the practice of hiring an external company to handle certain business functions, such as data center services, instead of managing them in-house.
What is in-house management?
In-house management refers to the practice of managing business functions, such as data center services, within the company rather than outsourcing them to an external provider.
What are the benefits of outsourcing data center services?
Outsourcing data center services can provide cost savings, access to specialized expertise, improved scalability, and increased flexibility.
What are the benefits of in-house management of data center services?
In-house management of data center services can provide greater control, better security, and more customization options.
What are the potential risks of outsourcing data center services?
Potential risks of outsourcing data center services include loss of control, security concerns, and potential communication issues with the external provider.
What are the potential risks of in-house management of data center services?
Potential risks of in-house management of data center services include higher costs, lack of specialized expertise, and limited scalability.
How do I decide whether to outsource or manage data center services in-house?
The decision to outsource or manage data center services in-house should be based on factors such as cost, expertise, scalability, control, and security. A thorough analysis of these factors can help determine the best approach for your business.